Hydroponics has become an increasingly popular method for cultivating plants without soil, capturing the interest of gardeners and commercial growers alike. This way to grow uses a nutrient-rich solution to feed plants, allowing for precise control over their environment. Yet, a common concern arises: How are plants protected from drowning when their roots are submerged in water?
The secret lies in the careful regulation of water oxygen levels and the strategic design of the hydroponics system. Oxygenation keeps the roots healthy, allowing them to thrive by facilitating necessary respiration processes. This ensures that plants receive ample oxygen while still being immersed in a nutrient solution that encourages optimal growth.
Keeping roots aerated is crucial in avoiding the issue of plant drowning. With technology and monitoring, hydroponic systems provide a balance between water and air, keeping roots healthy and plants robust. This approach is key to hydroponics, where roots adapt to remain partially submerged, benefitting from both water and oxygen.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics regulates oxygen levels to prevent root drowning.
- Nutrient solutions are carefully balanced for plant health.
- Monitoring technology supports optimal plant growth.
How Hydroponics Works
Hydroponic growing is an innovative method that allows us to grow plants without soil by using nutrient-rich water solutions. This technique involves inert growing media such as coconut coir, LECA, rockwool, and perlite, which provide support to the plants' roots.

In hydroponic systems, we ensure a continuous supply of water, nutrients, and light plants need to grow. One primary advantage is the prevention of overwatering problems that occur in soil-based systems.
Types of Hydroponic Systems:
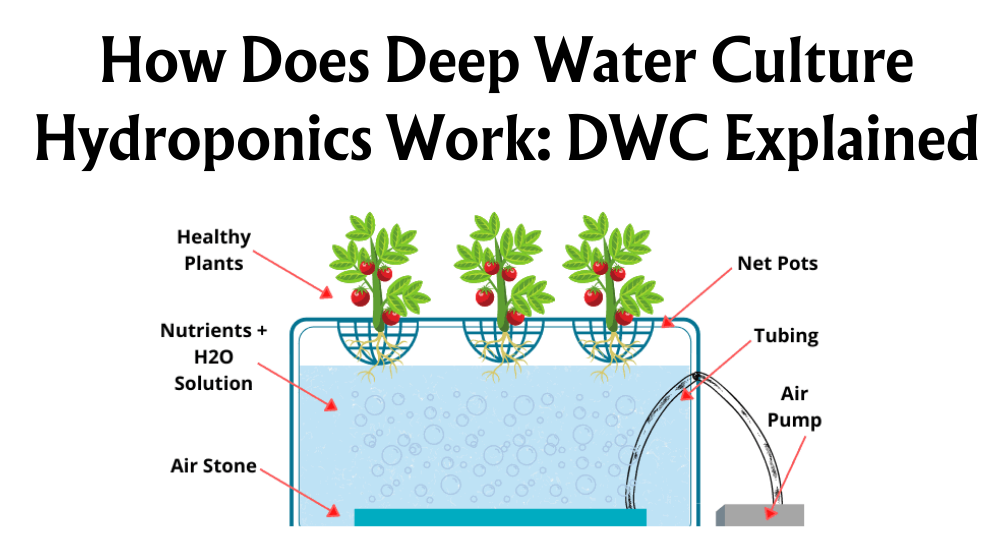
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants grow with roots submerged directly in oxygenated nutrient-rich water.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient solution flows over roots, providing nutrients and oxygen.
- Ebb and Flow: Nutrient solution floods the tray temporarily and then drains away, simulating natural rain cycles.
- Drip System: Nutrients drip onto each plant at a controlled rate, providing precise feeding.
- Wick System: Nutrients are drawn up to plants through a wick; optimal for small systems.
- Aeroponics: Roots are suspended in air and misted with nutrient solution for maximum aeration.
Each system ensures that the roots receive adequate oxygen, preventing plants from drowning. As such, plants in hydroponic systems tend to achieve faster growth and potentially higher yields compared to traditional soil methods.
The Role of Oxygen in Hydroponics

Importance of Root Oxygenation
In hydroponics, roots require a steady supply of oxygen for respiration, which is vital for nutrient uptake and plant health. Without sufficient oxygen, plants may experience root diseases and decline.
Methods to Ensure Adequate Oxygen Supply
Aeration techniques are crucial. We employ air stones and air pumps to introduce oxygen into the nutrient solution, ensuring roots have access to what they need.
Diffuser tubes and rings are effective tools. They help distribute oxygen evenly throughout the system, preventing any areas from becoming deficient.
System Design Considerations
Maintaining the correct amount of water is crucial for oxygenation. By preventing complete root submersion, we minimise the risk of oxygen deprivation.
Incorporating air gaps, as seen in systems like the Kratky method, allows roots to access additional oxygen. This design strategy supports healthier root development and overall plant vitality.
Nutrient Solution Management
In hydroponics, managing the nutrient solution is vital to prevent plants from drowning and ensure healthy growth. Our nutrient solutions involve a balanced mix of essential macro and micronutrients tailored to meet the specific needs of various plants. This precision helps keep the plant performing optimal metabolic processes.

One key factor in nutrient solution management is maintaining optimal oxygen levels. We regularly monitor dissolved oxygen levels to ensure that the roots receive adequate oxygen. By adjusting our aeration methods, we can guarantee consistent oxygen availability to the plant roots.
Preventing root rot is another critical aspect of nutrient solution management. We keep the nutrient solutions at appropriate temperatures to retain dissolved oxygen, which helps in maintaining healthy root systems. Additionally, we regularly clean and sterilise the system components to prevent the buildup of pathogens, safeguarding the plants from infections.
Organising the delivery of nutrient-rich water is essential for preventing waterlogging. Our systems employ various techniques such as timed nutrient delivery and drainage systems to manage water levels effectively. This structured approach ensures that the root system is never completely submerged, helping to avoid drowning the plants.
In summary, effective management of nutrient solutions in hydroponics requires precision and attention to detail. By optimising nutrient composition, maintaining oxygen levels, preventing root rot, and ensuring proper nutrient delivery, we create an environment conducive to plant health and growth.
Root Structure and Adaptation
In hydroponic systems, plant roots exhibit unique adaptations to thrive in water-based environments. One critical adaptation is the development of air roots. By having sections of the root system exposed to the air, hydroponic plants enhance their oxygen uptake.

Growing mediums such as perlite, rockwool, and vermiculite play a crucial role in supporting root structure. These materials provide stability while allowing roots to breathe and access oxygen. This is essential in preventing root rot, a common issue when roots are fully submerged and deprived of air.
Additionally, materials like coconut coir and expanded clay pebbles, also known as hydroton pebbles, are popular choices. They offer excellent moisture retention and aeration, crucial for hydroponic plants' root systems. Using a growing medium ensures that roots have the structure and environment needed to adapt effectively.
As roots adjust to hydroponic conditions, they tend to become more fibrous. This fibrous nature improves nutrient absorption, enabling plants to access essential nutrients efficiently. The adaptability of roots enhances their capacity to thrive in nutrient-rich, oxygenated water systems.
By selecting the right growing mediums and creating optimal conditions for root exposure to air, we can support plant health and development. This careful balance helps hydroponic plants avoid common pitfalls, such as root rot, ensuring a productive growing environment.
Technology and Monitoring in Hydroponic Systems
In hydroponic systems, technology plays a crucial role in ensuring plants receive the optimum conditions for growth. One key component we utilise is air pumps. These pumps operate continuously to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the nutrient solution. By doing so, they prevent the roots from suffocating, ensuring healthy plant development.

Effective monitoring is essential for successful hydroponics. We use dissolved oxygen meters to track oxygen levels within the nutrient solution. Additionally, sensors for temperature and pH are crucial. These tools allow us to maintain optimal environmental conditions, ensuring the various factors affecting plant health are kept in check.
The integration of automation and control systems simplifies the management of hydroponic environments. By automating processes such as aeration, nutrient delivery, and environmental parameter regulation, we can concentrate on enhancing plant yield and health. Smart technology, including IoT devices, further enhances the efficiency and precision of these systems.
In addition to these technological advancements, grow lights offer an indispensable advantage, compensating for natural light insufficiencies. By providing a consistent and suitable light spectrum, grow lights aid in extending the photosynthesis process, ultimately contributing to healthier and more robust plant growth.
By leveraging these technologies and monitoring tools, we increase the efficiency of hydroponic systems, reducing manual intervention and improving plant health outcomes. Continuous enhancements in this field hold promise for even more sophisticated and efficient cultivation techniques in the future.
Conclusion
In hydroponic gardening, we prevent plant drowning by ensuring water is constantly oxygenated and circulated. Our systems use air pumps, air stones, and diffusers to maintain optimal oxygen levels. This allows roots to breathe and take in necessary oxygen for healthy growth.
Hydroponic systems are engineered with precision. Models like the nutrient film technique and deep water culture carefully balance water and air exposure, keeping roots partially submerged for better aeration.
We should be eager to embrace the possibilities of hydroponics. By understanding its core principles and incorporating best practices, we can achieve efficient and sustainable gardening. Exploring this method may lead us to discover new potential in cultivating plants.






 Store Locator
Store Locator