Hydroponics is gaining traction as a prominent alternative in agriculture, and as we dive deeper into this innovative method, we find ourselves asking: Can hydroponics truly replace traditional soil-based farming? It's a question worth considering as factors such as land scarcity and sustainability pressure grow. While it's unlikely that hydroponics will completely replace traditional farming, it certainly has the potential to revolutionise food production, offering unique advantages over conventional methods.
Our exploration will delve into the remarkable benefits of hydroponics, like its ability to produce crops in smaller spaces, thanks to vertical farming techniques. Many urban areas, where land is scarce and expensive, could see a shift towards this practice due to its efficiency and adaptability. But amongst all these exciting developments, the real intrigue lies in whether this modern method can sustain our growing population while addressing ecological concerns.
As we navigate through the fascinating intersection of technology and agriculture, we're excited to explore what hydroponics can offer toward a sustainable future. Hydroponics may not provide a complete replacement for traditional farming, but its potential in redefining how and where we grow food is both promising and challenging.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics uses vertical farming for efficient space use.
- Ecologically advantageous but not a full replacement.
- Potential for sustainable urban farming solutions.
What Is Hydroponics?
Let's talk about hydroponics, a fascinating way to grow plants without soil. Instead, we use nutrient-rich water to feed the plants directly. This method can produce outstanding results, and it has truly revolutionised how we think about farming.

Several systems make hydroponics effective:
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Plants are suspended in a shallow stream of nutrients constantly flowing over their roots.
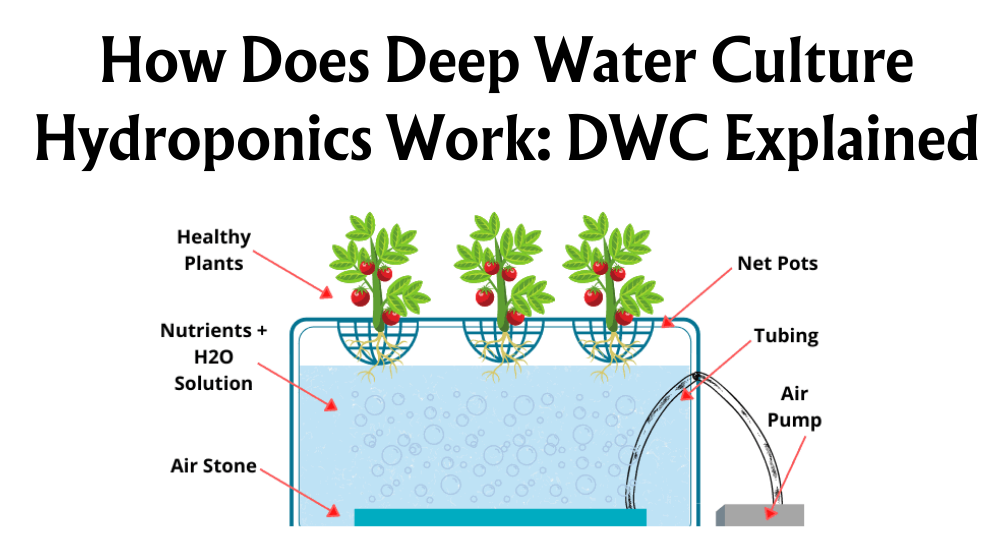
Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants are placed in a nutrient solution with roots submerged in water containing oxygen.
Aeroponics: Plants are suspended in air, and their roots are misted with a nutrient solution.
Ebb and Flow: This technique floods the plant roots with nutrient solution periodically, then drains it away.
What's super interesting is the history behind hydroponics. Did you know that early examples include the Hanging Gardens of Babylon? It's not just a modern innovation!
For the growing medium, things like coconut coir and perlite are often used. These materials provide support to the plant roots. They help facilitate better root aeration and nutrient absorption.
The commercial aspect of hydroponics has grown rapidly thanks to these modern techniques. As we continue exploring these methods, we're uncovering new ways to produce food efficiently and sustainably. It's an exciting time for us, considering how these innovations could influence future farming practices.
Ecological Advantages To Hydroponics
Hydroponic systems offer significant ecological benefits that can transform modern agriculture. By optimising resource use, including water and space, we can minimise environmental impact and increase efficiency. Hydroponic farming allows crops to grow quickly and with greater control, reducing the need for harmful pesticides and potentially lowering greenhouse gas emissions.

Fast Growth
With hydroponics, plants often enjoy a faster growth cycle compared to traditional farming. This is largely because the nutrient-rich water solutions deliver essential nutrients directly to the roots. This direct nutrient delivery lets plants absorb what they need more efficiently, reducing the time they take to mature.
Controlled environment settings shield plants from unpredictable weather, allowing a consistent growth rate across all seasons. Growing in these environments can mean higher yields and potentially more harvest cycles per year. This not only boosts productivity but can also shorten the time between planting and harvesting, enabling quicker responses to market demands and food shortages.
Cleaner Grow Environment
One of the major advantages of hydroponic farming is the cleanliness of the growing environment. Traditional soil contains a wide array of organisms and contaminants, but hydroponic setups eliminate the need for soil altogether. This results in fewer pest infestations, naturally cutting down the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides.
As these systems are often placed indoors, away from contaminated environments, there is less risk of pollutants affecting the crops. The result is cleaner produce with fewer chemical residues, benefitting both consumers' health and the environment. This approach to growing can help us meet the increasing demand for safer and cleaner food sources.
Uses Less Harmful Pesticides
By using controlled indoor environments, hydroponics significantly reduces the need for pesticides. Pest management is primarily done through mechanical means, like netting and good hygiene practices, rather than chemicals. This leads to healthier crops with fewer pesticide residues.
The environmental impact of reducing pesticide use is substantial. Fewer chemicals leach into the soil and water systems, conserving biodiversity and promoting healthier ecosystems. Additionally, some hydroponic farms utilise biological pest control, which minimises the need for synthetic compounds altogether, enhancing sustainability.
Greater Control
Hydroponics offers unparalleled control over nutrient levels and growing conditions. Farmers can precisely adjust nutrient solutions to meet the specific needs of different plants. This targeted approach reduces waste, optimising the consumption of resources and promoting efficient growth.
This greater control extends to the climate within the growing area, allowing temperature, humidity, and light to be meticulously regulated. By integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, we can further reduce the carbon footprint of hydroponic farming. This adaptability not only enhances yields but also allows farming in areas where traditional agriculture is not viable, promoting sustainability in agriculture.
Can Hydroponics Replace Soil Farming?
Hydroponics is an innovative method that offers potential to significantly improve farming practices. One of its standout features is its ability to increase crop yields by enabling year-round cultivation. This makes it a promising option for urban farming and regions with unsuitable climate conditions.
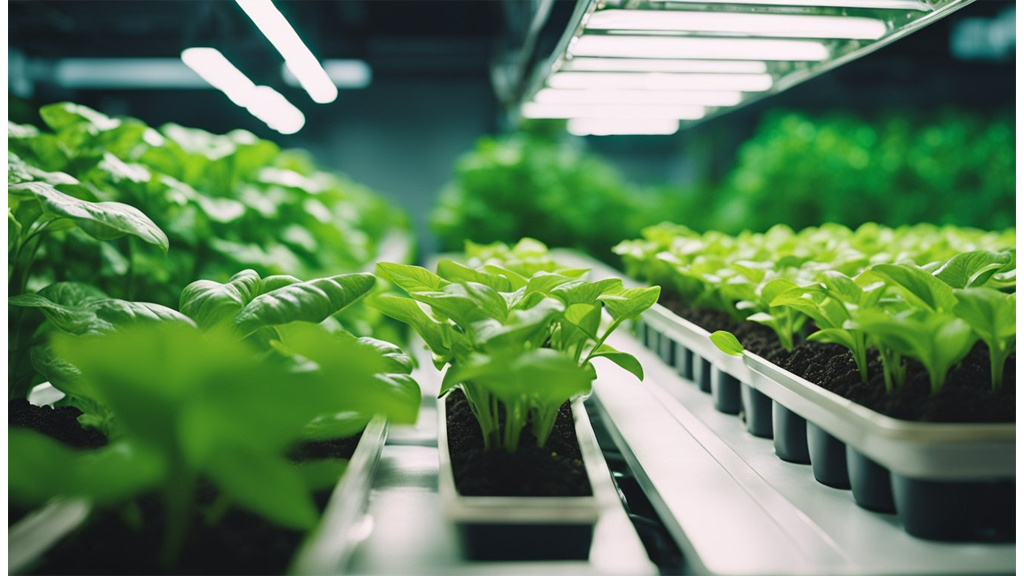

Space efficiency is another critical advantage of hydroponics. By limiting land use, hydroponics supports the development of vertical farming systems. These systems minimise the space requirements traditionally associated with soil farming, making them ideal for cities. This is particularly important for producing fresh produce where land is scarce.
While hydroponics can reduce soil-related issues like soil degradation and soil erosion, not all crops are currently suitable for this method. The focus is primarily on high-value and fast-growing plants, such as leafy greens and herbs. Yet, technological advancements are constantly expanding the range of crops.
The initial setup costs for hydroponic systems can be quite high, and there may be ongoing expenses related to energy and maintenance.
Hydroponics allows us to use resources more efficiently. It requires less water than traditional irrigation practices, reducing the stress on water resources. By eliminating the need for ploughing and fertilising soil, it also decreases chemical use and helps improve the overall health of our environment.
While it may not be able to fully replace traditional agriculture, hydroponics holds great potential to complement and supplement traditional methods, particularly in urban areas with high demand for fresh produce. Ultimately, it's a fascinating possibility we should continue to explore and integrate into our farming practices.
Hydroponics and Sustainability
When we discuss hydroponics, we're really talking about an innovative approach to sustainable agriculture. At its core, hydroponics enhances food security by enabling urban agriculture. This means we can produce fresh crops locally, cutting our reliance on distant farms. Imagine alleviating food deserts in cities by growing produce right where people live.
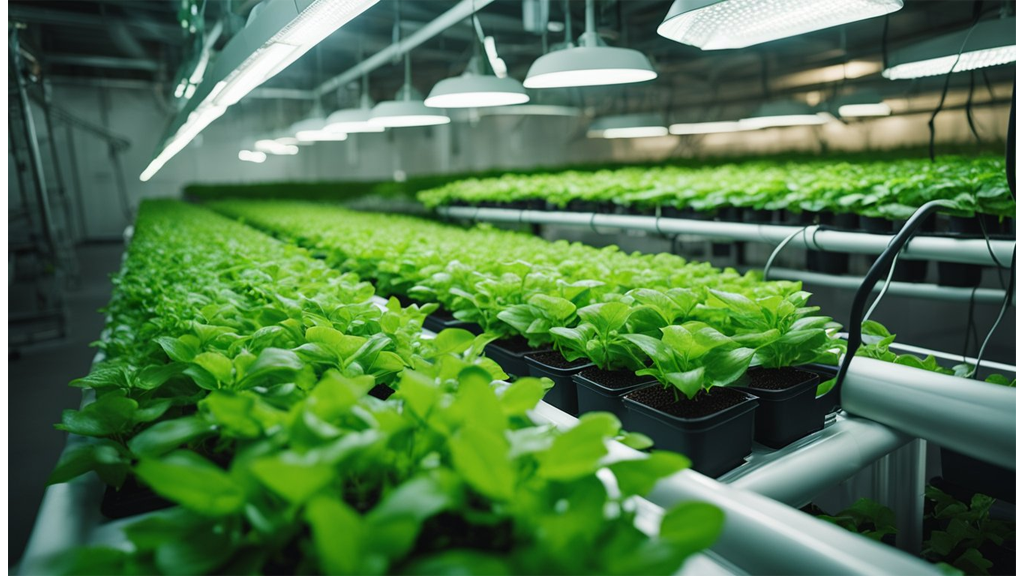

Climate change and extreme weather are real threats to traditional farming. Fortunately, hydroponics shields our crops in controlled environments, making them more resilient to such impacts. The best part? We can grow produce year-round, so there's always a reliable supply of food. This is a key factor in addressing global hunger.
Scalability is a standout benefit. We can install hydroponic systems virtually anywhere, particularly in regions where arable land is scarce. Think about communities that struggle with food scarcity – hydroponics can help provide them with fresh, nutritious produce.
In many urban centres, we've seen projects successfully integrate hydroponics to boost food security. Non-profit organisations in developing countries are also employing hydroponics to fight hunger, showcasing its global potential. Through case studies, these efforts demonstrate how innovative practices can make a tangible difference.
Conclusion
As we look at the integration of hydroponics in modern agriculture, there are several key benefits to highlight. Hydroponics uses precise nutrient control, which helps plants grow efficiently and can work well even in areas with limited land. This method is especially significant in urban areas where space is scarce.
Water scarcity is a growing issue across the globe. Hydroponics can offer a solution by being incredibly water-efficient, using only about 10% of the water required by traditional farming. This is a crucial advantage for areas struggling with water shortages.
Food security is another vital concern. With the ability to produce crops year-round, hydroponics can help ensure a stable food supply, even in regions with harsh climates or poor soil quality.
Yet, as promising as hydroponics is, it does have its challenges. The initial costs can be steep, and there's a need for ongoing research to enhance its applicability. For food safety, close monitoring of nutrient solutions is necessary to ensure healthy crops.
We believe the future of farming lies in the collaboration between traditional methods and hydroponics. By embracing both, we can address the challenges of food security, water scarcity, and food safety. Let’s continue exploring and refining these technologies to build a resilient agricultural system.






 Store Locator
Store Locator