Hydroponics offers an innovative and efficient alternative to traditional soil farming, allowing us to grow plants using nutrient-rich water. We've seen a surge in interest in this method as it provides a sustainable way to cultivate crops, especially in regions facing land and water constraints. By recirculating water, hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional agriculture, making it an appealing option for areas prone to drought.
As gardeners, the allure of hydroponics lies in its potential to produce high-quality and nutritious produce in various climates, regardless of seasonality. More farmers are adopting hydroponics to meet the rising demand for locally sourced food and to minimise the environmental footprint. Technological advancements have further facilitated this interest, with systems now available for both commercial and home use.
This growing revolution is characterised by adaptable setups, which allow for the cultivation of plants indoors or outdoors, and even vertically. The efficiency, predictability, and sustainability of hydroponic systems have captured our attention, ensuring that this method will continue to be an exciting development in agriculture.
What Is Hydroponics?

Hydroponic growing is an innovative method where plants grow in water enriched with nutrients instead of traditional soil. This ancient technique, practiced by the Babylonians and now vital in modern agriculture, utilises roots submerged in a nutrient-rich solution, providing steady and controlled plant growth.
Hydroponic Farming Characteristics
No Soil Needed
In hydroponics, plants thrive without soil by using water and nutrients delivered directly to their roots. Media such as clay pellets or rockwool support the plants without soil, maximising space and reducing weed-related issues.
Closed-Loop System
Hydroponic systems often feature a closed-loop system, where water and nutrients are recirculated, conserving resources. This focus on reusability can lead to a reduction in water usage by up to 90% compared to soil-based gardening.
Automation
Automation plays a crucial role in efficient hydroponic setups. By integrating pumps and timers, we can optimise the delivery of nutrients and water, ensuring ideal growing conditions at all times. This reduces manual intervention and enhances precision.
Hydroponic Systems
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT provides a thin nutrient solution stream across plant roots. It's cost-effective but not ideal for larger plants.
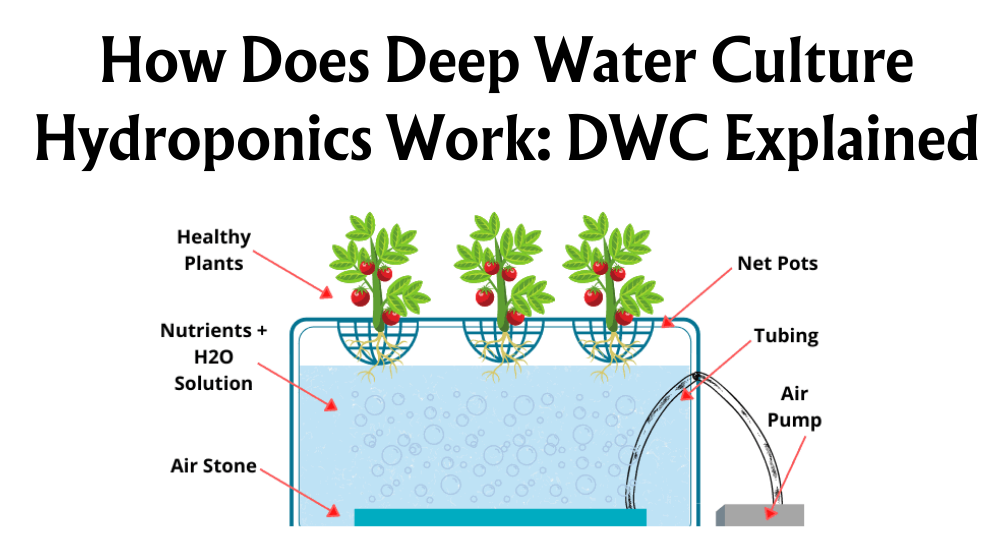
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
DWC systems submerge roots in nutrient-rich water. It's beginner-friendly and provides rapid growth, yet requires constant oxygen supply.
Wick Systems
In wick systems, plants draw nutrients through a wick. It's simple and passive, yet less effective for larger crops.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics suspends roots in air, spraying them with nutrients. It promotes rapid growth but needs precise management and higher initial costs.
Each technique suits different needs, making hydroponics adaptable for various crop types and scales, from small indoor gardens to expansive vertical farms.
Hydroponic Plant and Crop Types

When it comes to hydroponics, we find that certain plants thrive particularly well. Leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach are extremely popular. Their rapid growth and small space requirements make them ideal candidates. These greens provide a continuous harvest, which can be especially profitable in a commercial setting.
Besides greens, various herbs like basil, mint, and cilantro excel in hydroponic gardens. They grow quickly and are in high demand, particularly in culinary markets, offering a fresh supply year-round. This makes them a wise choice for both home growers and commercial farmers.
Tomatoes and strawberries are high-value crops that perform well hydroponically. By growing them without soil, we can avoid some soil-borne diseases and pests. This method allows for efficient use of resources, leading to impressive yields. Many farms have reported successful results, showcasing their potential.
Further diversifying, hydroponic systems can be tailored to support watercress and some veggie types. This includes cucumbers and peppers, which thrive in a controlled environment. The ability to adjust nutrient solutions allows us to cater to the specific needs of each plant type accurately.
Fish integration, often referred to as aquaponics, presents a unique angle. We combine fish farming with plant cultivation, where fish waste acts as a natural fertiliser. This method can efficiently grow leafy greens and other compatible crops, making it an intriguing option for sustainable farming.
Overall, hydroponics offers a flexible approach, allowing us to cultivate a variety of plants, ensuring a sustainable and productive future.
Benefits of Hydroponics

Faster Growth and Higher Yields:
In hydroponics, plants generally grow faster because nutrients are directly delivered to the roots in an optimised manner. We've noticed that many growers experience significantly increased yields within shorter timeframes compared to traditional farming. This accelerated growth is achieved without compromising the quality of produce.
Water Efficiency:
Hydroponics is remarkably water-efficient, using up to 90% less water than conventional farming methods. This is vital in a world facing water scarcity. Many urban farms and large-scale operations are successfully implementing hydroponic systems to minimise water waste and enhance sustainability.
Space-Efficiency:
One of the standout features of hydroponics is its space-saving design. Systems like vertical hydroponics enable high-density planting in compact areas. We often see rooftop hydroponic systems thriving in urban settings, maximising space use and increasing production in limited areas.
Reduced Pesticide and Chemical Use:
Hydroponic farming typically faces fewer pest problems due to its controlled environments, reducing the need for pesticides and harmful chemicals. This offers significant benefits for health-conscious consumers who seek organic and sustainable food options.
Environmental Impact:
Hydroponics contributes to a lower carbon footprint, as plants can be grown locally and without soil, reducing transportation needs and soil degradation. Many eco-conscious farming operations successfully demonstrate reduced environmental impacts through their innovative hydroponic techniques. This method provides an avenue for sustainable agriculture while ensuring fresh and nutritious produce.
Drawbacks Of Hydroponics

Initial Setup Costs:
Hydroponics demands a considerable upfront investment. Essential equipment like pumps, grow lights, and reservoirs can be pricey. Starting small or exploring DIY systems might help ease the financial burden.
Complexity and Maintenance:
Managing a hydroponic system can be complex. We must constantly monitor water pH, nutrients, and conduct regular system maintenance. Issues such as nutrient imbalances, clogging, and equipment failure can arise, requiring careful attention.
Learning Curve:
Adapting to hydroponics involves a steep learning curve. Beginners need time to confidently manage nutrient solutions and pH levels. Fortunately, there are workshops, online guides, and a supportive community to help us along the way.
Dependency on Chemicals:
Unlike traditional farming, hydroponics is heavily reliant on nutrient solutions. This can involve the use of chemicals to ensure plants receive the necessary nutrients normally found in soil. Monitoring is essential to avoid issues like nutrient deficiencies.
Labour Intensive:
While traditional farming requires physical labour in the fields, hydroponics involves a different kind of work. We may spend a significant amount of time in system maintenance and monitoring. This can include addressing common issues like algae formation or clogs in equipment.
Energy and Resource Use:
Hydroponics needs continuous access to electricity and a clean water supply. This dependency might be a challenge in areas with limited resources. It's critical for us to ensure there's a consistent energy source to keep our systems operational.
Hydroponics or Organic: Differences

Soil vs. Water:
When considering nutrient sources, organic farming relies on soil and natural fertilisers. These promote plant health through processes like crop rotation, which enriches soil quality over time. In contrast, hydroponics uses synthetic nutrients dissolved in water, providing plants with a precise nutrient mix. This approach can be especially beneficial for gardening in urban areas with limited space.
Environmental Considerations:
Hydroponics might not use natural soil, but it can be sustainable by optimising water usage. Systems often recycle water, reducing waste—a clear advantage in regions facing climate change challenges. Moreover, organic farming emphasises maintaining soil health and minimising pesticide use. Yet, hydroponics allows for controlled pest management without resorting to heavy chemical applications.
Cost and Accessibility:
The cost dynamics between these farming methods vary significantly. Organic produce can be more expensive due to soil management needs and organic pesticide costs. On the other hand, hydroponics, particularly for urban agriculture, may reduce operational costs in the long run by cutting down on water and space requirements. This can make hydroponic systems attractive for small-scale urban growers and those in regional diversity contexts.
Incorporating both systems might suit different needs: organic for those valuing traditional farming methods and hydroponics offering practical solutions for urban settings. Each has its niche, and finding the right balance could help us address the diverse needs of agriculture today.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our discussion on hydroponics, let's underscore why this growing method stands out. Hydroponics is a solution where crops can achieve faster growth rates compared to traditional farming.
Another major advantage involves the efficient use of resources. Water usage is dramatically reduced, with some systems utilising up to 98% less water. This makes hydroponics ideal for regions facing water shortages. In terms of space, hydroponic setups allow us to grow more in less area—perfect for urban environments.
There's also a reduction in pesticide use. Since plants are grown in controlled environments, the need for harmful chemicals diminishes. This not only benefits the planet but also enhances the quality of our produce.
With rising food prices and limited natural resources, hydroponics presents a viable alternative for sustainable agriculture. We're seeing a shift towards urban farming, where fresh produce is grown closer to where people live, cutting down on transportation emissions and costs.
Let's consider adopting hydroponics to embrace a more sustainable approach to farming. Whether you're new to gardening or looking to expand your existing setup, hydroponic solutions offer numerous benefits.
We can start small or go big; the choice is ours. Why not transform our growing habits and contribute positively to our environment?






 Store Locator
Store Locator