Which Countries Use Hydroponics
Imagine growing fresh produce without a garden or soil, right inside your home or in a bustling urban centre. This is the magic of hydroponics, a revolutionary soil-free farming method that is used to grow plants in controlled environments. As our world faces increasing food demands and space constraints, hydroponics offers a sustainable and efficient solution. Numerous countries in the world, and even densely populated regions are turning to hydroponics to boost food security.
Globally, the hydroponics market size continues to grow. In developing countries, hydroponics has proven beneficial, offering solutions that improve nutrition using limited resources. Programmes in places like Ecuador are showing promising results. Especially in improving children's diets with easier access to hydroponically grown fresh cucumber and leafy vegetables like lettuce.
The promise of global hydroponics extends far beyond its immediate benefits. Countries worldwide are taking an ever-growing market share. As we explore which nations are embracing this technology, we uncover a rich tapestry of innovation, need, and opportunity that continues to shape the future of food production.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics enables soil-free, controlled environment farming.
- Countries like Canada and South Africa are utilising hydroponics.
- Developing regions are adopting hydroponics for food security.
How Does Hydroponics Work?

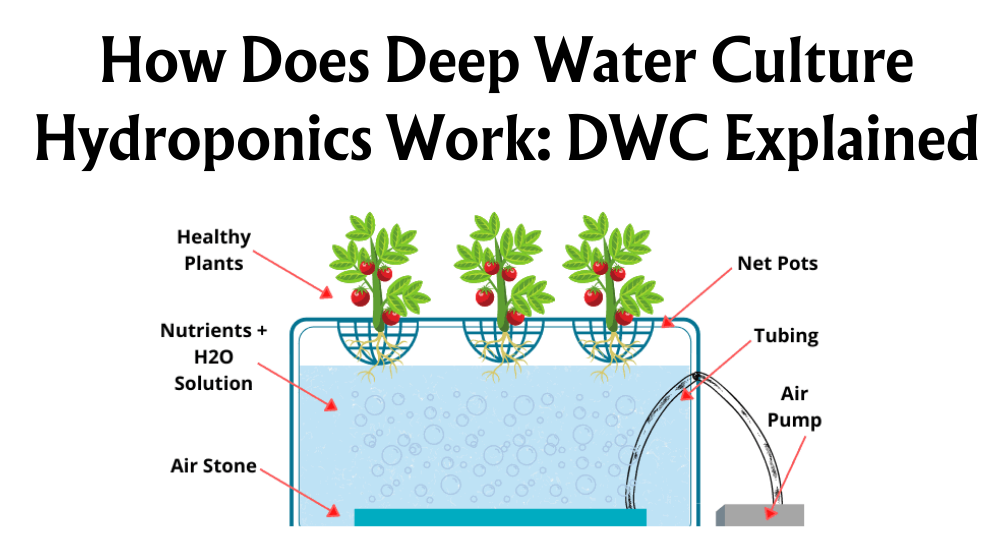
Hydroponics offers a fascinating method to grow plants using water-based solutions rich in nutrients. It's an alternative to traditional soil-based gardening. In these systems, we often find plants rooted in materials like coconut coir, perlite, or rock wool to provide stability.
Nutrient-rich water flows around the plant roots, giving them access to the essential elements they need. This method reduces water usage and allows for year-round cultivation, as it's typically done in controlled environments.
Here are some types of hydroponics systems we commonly encounter:
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique): A thin film of nutrient solution runs over the plant roots, aiding continuous nutrient uptake.
- Drip Systems: Nutrients are distributed to each plant through a network of small tubes, making for highly effective delivery.
- Wick Systems: The simplest method where a wick draws nutrients from a reservoir to the plant roots.
The key advantages of using hydroponic systems include more efficient resource use—particularly crucial in regions with limited water and arable land. For instance, in places like Jordan and Libya, hydroponics minimise water consumption, making it a sustainable choice in resource-scarce environments.
Furthermore, environmental control in hydroponics allows us to manage factors such as temperature, humidity, and light. This results in healthier plants and optimises growth conditions while offering some protection against pests and unfavourable weather conditions.
By embracing these innovative techniques, we're witnessing a more sustainable, efficient, and reliable approach to the agriculture industry that holds great promise for the future.
What Makes Hydroponics Popular

Hydroponic farming methods have gained popularity due to their ability to address critical challenges like food security, profitability, and environmental concerns. This method of growing plants without soil allows for efficient resource use, making it appealing across diverse climates and economic contexts.
Focus On Food Security
In areas with harsh climates, hydroponics provides a reliable method for producing food. Countries experiencing frequent droughts or those heavily reliant on food imports can benefit immensely. By using hydroponics, they can cultivate crops without the need for fertile soil, significantly reducing dependency on traditional agriculture.
For instance, regions such as the Middle East and North Africa have embraced hydroponics to bolster food security. These areas often face water scarcity and unsuitable soil conditions, making hydroponics an attractive alternative for stable food production.
Profitability
The commercial potential of hydroponics is significant, largely due to its high-yield capacity. By optimising the resources needed for plant growth, hydroponics allows growers to maximise output while minimising waste. This efficiency translates into higher profit margins for commercial operations.
A notable example of this is Singapore. The country has heavily invested in urban farming technologies, including indoor hydroponic systems. These setups have proven advantageous by increasing crop yields while using limited space, aligning well with Singapore's focus on food sustainability and economic efficiency.
Eco-Friendly
Hydroponics is renowned for its environmentally friendly attributes. By drastically reducing water usage compared to traditional farming methods, hydroponics presents a viable option for sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, this practice decreases the need for chemical pesticides, contributing to a healthier ecosystem.
Germany showcases a commitment to these eco-friendly principles by incorporating sustainable practices within vertical farming. The reduction of land disruption and the conservation of natural resources highlight hydroponics as a cornerstone of their sustainable strategies, aiding in the global effort to minimise agriculture's ecological impact.
Countries Using Hydroponics

Across the world, this method of farming has developed a substantial global hydroponics market boosting food production and ensuring sustainability. Each region has a unique adoption of hydroponics, focusing on local needs and environmental conditions.
North America
The United States and Canada are key market players in the hydroponic farming industry. They are leaders in this type of closed system technology and while their market is segmented, they are expected to reach ever greater market growth.
United States
American Hydroponics, in states like California and Arizona, is driven by favourable climates and large urban areas demanding fresh produce. One noteworthy example is New York's Gotham Greens, a large-scale operation located in urban environments using hydroponics to bring fresh, local produce to city dwellers. Urban areas benefit significantly, reducing the need for long supply chains and ensuring freshness.
Canada
Canada embraces hydroponics to extend the growing season, particularly in its colder regions. Utilising greenhouses and controlled environments, Canadian farmers can grow crops year-round. This not only aids in local food security but also reduces the reliance on imports, providing consistent access to fresh produce.
Europe
Europe boasts the largest market share of hydroponics. Here are two of the leading nations of hydroponics in Europe, bringing out the best in this kind of farming.
Germany
Germany is known for its focus on innovation and sustainability in hydroponics, with vertical farms growing rapidly in popularity. Berlin, for example, hosts several urban farms that employ eco-friendly infrastructure. These vertical farms help in maximising space efficiency and reducing the carbon footprint of food production, aligning with Germany’s emphasis on green technology.
France
France leads in city agriculture, especially with urban vertical farms and rooftop hydroponic gardens. These initiatives help in transforming city spaces into productive landscapes. By using innovative techniques, France continues developing urban farms to support city-dwellers needs for sustainable and local produce while integrating food production with everyday city life.
Middle East
UAE
The UAE focuses heavily on government initiatives aiming to improve food security through hydroponics. The Emirates spearheads projects that promote self-sufficiency, relying less on imports by using cutting-edge technology in controlled environments. Such projects directly address the challenges of food production in arid regions.
Jordan and Libya
In Jordan and Libya, various efforts support food security in challenging, arid climates. Several pilot projects utilise hydroponics as a means to combat food scarcity. Despite facing numerous difficulties, these projects have seen successes, showcasing hydroponics as a viable solution to improve food production in harsh environments.
Asia
China
China embraces large-scale hydroponic production to meet the demands of its vast population. Leveraging tech-driven farming innovations, China is enhancing efficiency and yield, making significant strides in agricultural technology. This approach helps address both urban and rural needs.
Japan
Japan uses hydroponics efficiently within limited urban spaces, often employing LED-based indoor farms. These setups optimise light and energy usage, making them ideal for densely populated cities. This sustainable model not only supplies fresh produce but also serves as a blueprint for densely populated areas worldwide.
South Korea and Taiwan
South Korea and Taiwan lead in implementing cutting-edge vertical farms. These farms integrate smart technology, allowing for precise control over growing conditions, and enhancing productivity. This emphasis on integration ensures optimal outputs despite environmental challenges.
Singapore
In Singapore, government investment in self-sustaining solutions prioritises indoor hydroponics. With limited land, Singapore focuses on maximising output from small areas, contributing significantly to its goals of food security and sovereignty by incorporating advanced hydroponic technology.
Thailand
Thailand combines traditional farming methods with modern hydroponics to support its agriculture sector. By blending these techniques, Thailand enhances crop yield and reliability, providing a stable food supply for its population using a balanced approach.
Conclusion
In recent years, the hydroponics industry has gained significant attention as an innovative solution to global food security and sustainability challenges. This soil-free farming technique allows us to grow plants efficiently, using less water and space. Countries across the world including USA, Japan, and the Netherlands are leading the way in large-scale hydroponic production.
Opportunities for Home Growers:
Hydroponics isn't just for commercial farms. It's also accessible for home growers looking to cultivate fresh produce year-round. With the right guidance and tools, anyone can start their own hydroponic garden.
Tips for Beginners:
- Essential Accessories: Grow lights, pH meters, and nutrient solutions.
- Useful Tools: Timers and automated watering systems.
- Feeds and Mediums: Coco coir and perlite are excellent for plant support.
Through the adoption of hydroponic systems, we can contribute to a more sustainable future. Whether large-scale or small, every effort makes a difference.






 Store Locator
Store Locator