Keeping our plants healthy and productive starts with giving them the right nutrients, tailored to how we grow them. To choose the correct nutrients for our growing method, we need to consider the type of plant, the specific growing media (like soil or hydroponics), and the nutrients vital for healthy development such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and key micronutrients like zinc and iron. For example, a high-nitrogen feed works well for leafy growth, while a balanced approach suits fruiting and flowering varieties.
Our 40 years of combined experience have shown us that attention to these essentials leads to stronger, more resilient plants. Whether we're gardening in soil, using containers, or experimenting with hydroponics, making informed nutrient choices ensures robust roots, vibrant leaves, and plentiful yields. Let’s break down exactly what our plants need and how to provide it efficiently, so our gardens can flourish.
Key Takeaways
- The right nutrients depend on plant type and growing medium.
- Essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are key for healthy plants.
- Tailoring nutrient choices boosts plant strength and yields.
The Importance of Plant Nutrition
When we talk about plant health, nutrition is at the core of everything. Plants rely on a careful mix of nutrients to thrive at every stage of growth. The right nutrients support strong stems, lush leaves, and vibrant blooms.
We often hear about nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—these are the primary nutrients most plants need in the largest amounts. Secondary nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulphur, as well as micronutrients including zinc and iron, also play key roles. A simple table helps clarify their importance:
| Nutrient Type | Examples | Role in Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Primary (macronutrients) | Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium | Growth, flower/fruit development |
| Secondary nutrients | Calcium, magnesium, sulphur | Cell strength, photosynthesis |
| Micronutrients | Zinc, iron, manganese, copper, boron | Enzyme function, overall health |
Proper sunlight works together with nutrients to boost photosynthesis and growth. Without enough light or nutrients, we might spot problems like yellow leaves or stunted development. These can be early signs of nutrient deficiencies.
If we get the balance wrong, either by providing too little or too much, plant health can suffer. Deficiencies can slow plant growth or produce visible issues like poor colour and weak stems. Toxicities from over-fertilising sometimes encourage unwanted weed growth or damage roots.
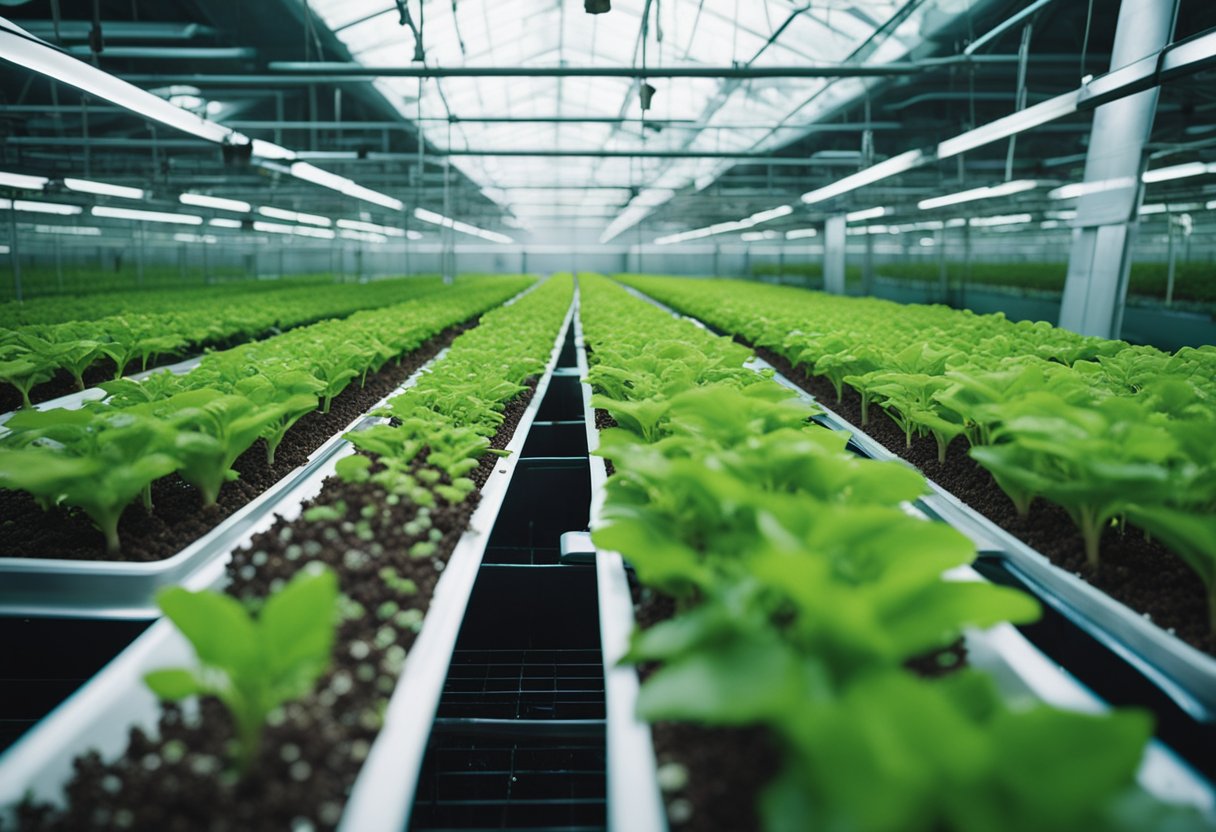
In hydroponic systems, nutrition matters more than ever. Plants take up their nutrients straight from water, so we need to be precise with dosages. A nutrient mix that's too weak leads to deficiency; too strong, and we risk harming the plants.
Staying aware of our plants’ nutritional needs lets us prevent problems and encourage healthy, robust growth. Short, regular checks help us catch and correct issues before they affect yield or overall vitality.
Essential Nutrients for Plant Growth
To help our plants thrive, we need to provide a careful balance of essential nutrients. Each type of nutrient plays a unique role in healthy growth, strong roots, and robust yield.
Macronutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, And Potassium
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—often labelled as N, P, and K—are the primary macronutrients found in almost every plant feed. When we look at a bag of fertiliser, those three numbers refer to the ratio of N-P-K.
- Nitrogen (N): This element is crucial for lush, leafy growth and is a major component of chlorophyll and plant proteins. Plants that lack nitrogen may display yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus helps our plants establish healthy root systems and encourages flowering and fruiting. A shortage leads to poor root development and weak stems.
- Potassium (K): Potassium builds resilience, aids in water regulation, and supports enzyme activation. With enough potassium, plants resist disease more effectively and can handle stress from the environment.
| Macronutrient | Main Function | Deficiency Sign |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Leaf growth, protein formation | Yellowing leaves |
| Phosphorus | Root growth, flowering | Weak roots, slow flowers |
| Potassium | Health, disease resistance | Brown leaf edges, weakness |
Besides these, calcium, magnesium, and sulphur act as secondary nutrients, stabilising cell walls and supporting vital enzyme functions. Trace elements like iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum, and chlorine complete the nutritional balance, even though we only need them in tiny amounts.
By understanding what each nutrient does, we can make informed choices that suit our growing methods and the specific needs of our plants.
Nutrient Management For Specific Plant Types
Selecting the right nutrients depends on what we are growing, as various plant types have unique needs to thrive. The composition and balance of fertilisers, organic matter, and micronutrients are critical for achieving reliable results.
Fruits
Fruiting plants, such as tomatoes and strawberries, require higher potassium levels to support fruit set and flavour. For example, when growing tomatoes hydroponically, we need to tailor our nutrient solution with increased potassium and balanced nitrogen and phosphorus. This approach promotes both fruit yield and quality.
Compost and well-rotted organic fertilisers help boost micronutrient levels and soil health. In traditional gardens, applying a tomato feed rich in potassium after the first fruits appear can significantly enhance productivity. Peas benefit from phosphorus early on, but once pods begin forming, potassium is more important.
Tip: Use a balanced complete fertiliser at planting and switch to one higher in potassium during fruiting for best results.
Vegetables
Leafy greens like lettuce and spinach grow best with lower nutrient concentrations. Too much nitrogen can cause leaf burn and thin texture, so we should use diluted liquid feeds or well-aged compost.
Root vegetables such as carrots and beetroot prefer a balanced blend of nutrients. If we use excessive nitrogen, we might get lush tops but poor roots. Bone meal is helpful for supplying phosphorus, promoting healthy root development.
When growing peas, we often improve the soil with compost and minimal additional feeding since they fix their own nitrogen. Organic methods, such as applying mulch, help maintain soil fertility and structure.
| Vegetable Type | Best Nutrient Approach | Organic Option |
|---|---|---|
| Leafy Greens | Diluted or frequent low feeds | Compost tea |
| Root Crops | Balanced NPK | Bone meal, compost |
| Legumes | Minimal added N, more P & K | Well-rotted compost |
Flowers
To boost flowering, we focus on phosphorus and potassium. Higher phosphorus supports bloom production, while potassium encourages lasting blossoms and disease resistance.
Magnesium and sulphur influence flower colour and aroma. For example, feeding flowering plants an Epsom salt solution (which contains magnesium) helps enhance colour vibrancy. We avoid excessive nitrogen, as it encourages green growth at the expense of flowers.
Organic flower growers often apply compost, bone meal, or specialised organic bloom fertilisers to support floral health and fragrance.
Pro tip: Apply a liquid bloom feed every two weeks for long-blooming annuals and perennials to keep flowers coming.
Ornamental Plants
Ornamental shrubs and foliage plants need a steady supply of balanced nutrients to maintain healthy leaves and attractive shapes. Regular monitoring is important—too much fertiliser can lead to leaf tip burn, while too little causes faded colour and weak growth.
Using slow-release fertilisers or organic compost is effective. We stay attentive to signs of deficiency or excess, such as yellowing leaves or leaf drop, and adjust our feeding schedule accordingly.
For plants in pots, nutrients leach out faster, so more frequent but weaker feedings work well. Ornamental grasses and evergreens benefit from a spring application of granular balanced fertiliser or organic mulch to help maintain vigour and foliage density.
How To Choose By Growing Media
Different growing media require specific approaches to nutrient selection and management. We need to match the right products and techniques with our chosen substrate to avoid deficiencies and ensure healthy plant development.
In Soil
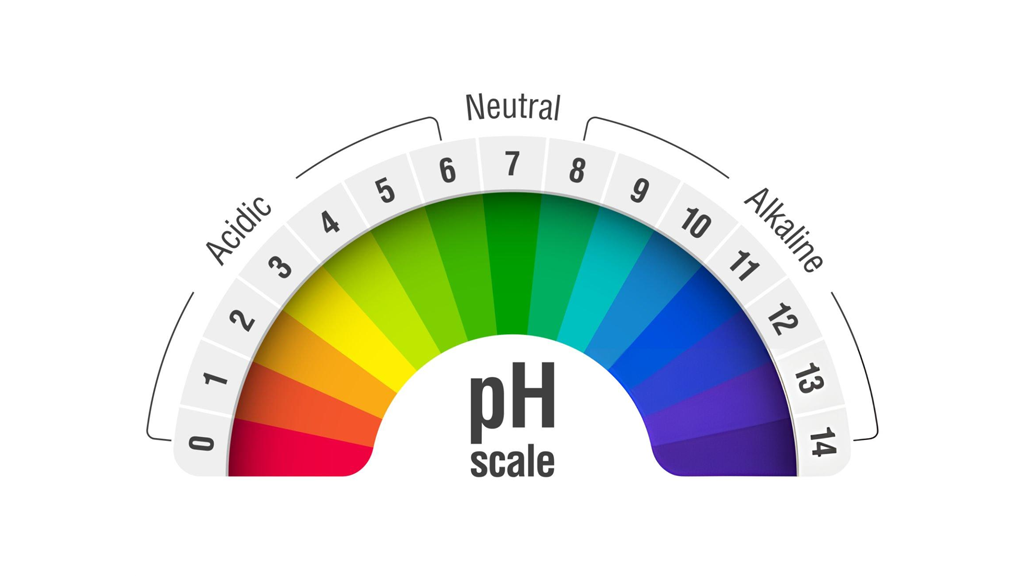
When growing in soil, our plant nutrition depends heavily on the soil structure, nutrient levels, and pH levels. It's a good idea to test the soil before starting, as different soils—like sandy, loamy, or clay—can affect how well plants can access water and nutrients. A basic soil test tells us about pH (most plants do well at pH 6-7), macronutrient levels, and organic matter.
Feeding plants in garden soil or potting mix often involves:
- Using slow-release fertilisers or top-dressing with compost
- Supplementing with liquid plant food for heavy feeders
- Adjusting the approach if using enriched potting mixes like Miracle-Gro
Soil texture also matters. Sandy soil needs more frequent but lighter fertiliser applications due to poor nutrient retention, while loamy soil offers a balanced nutrient and water-holding capacity. We should maintain soil fertility by rotating crops and adding organic material as needed.
In Coco Coir
Coco coir is popular for its excellent drainage and air-holding properties, but it holds onto calcium and magnesium, which can cause deficiencies if we’re not careful. Unlike traditional garden soil, coco has unique cation exchange properties, making it essential to use nutrient formulations designed specifically for coco.
Key considerations for coco coir:
- Always choose coco-specific nutrient lines
- Supplement with extra calcium and magnesium if your main feed lacks them
- Check that your fertilisers contain all essential micronutrients
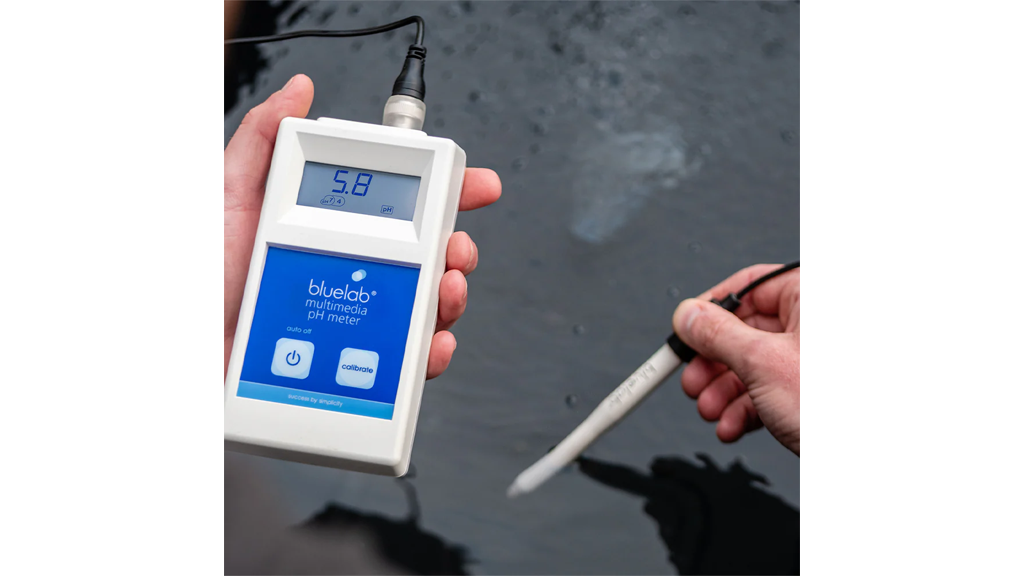
Since coco has little to no inherent fertility, we control all feeding. Typical feeding involves measuring the electrical conductivity (EC) and adjusting nutrient levels for each stage of growth. Keeping the pH between 5.8–6.2 helps with nutrient uptake and prevents lockout, so regular monitoring is vital.
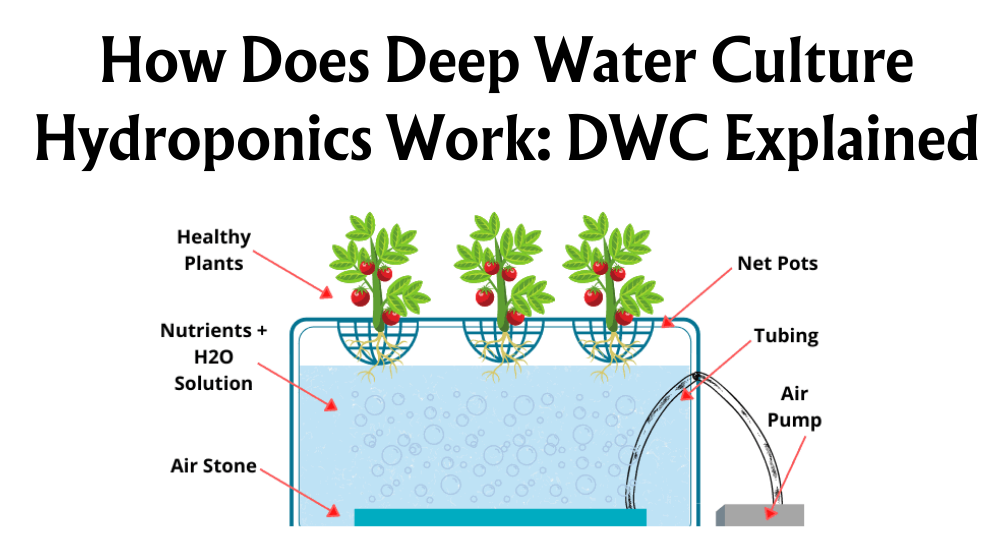
In Hydroponic Systems
With hydroponics, our plants rely entirely on water-soluble nutrients delivered directly through their water supply. There’s no buffering from existing soil, so the nutrient solution must be perfectly balanced. The most common approach is to mix commercial hydroponic fertilisers such as Optimum Hydroponix Optical, or to blend our own using calcium nitrate and magnesium sulphate.
Hydroponic nutrient management looks like this:
- Carefully measure out each fertiliser to match your plant’s needs
- Keep electrical conductivity (EC) between 0.8–1.5 for leafy greens
- Adjust EC for fruiting crops as required
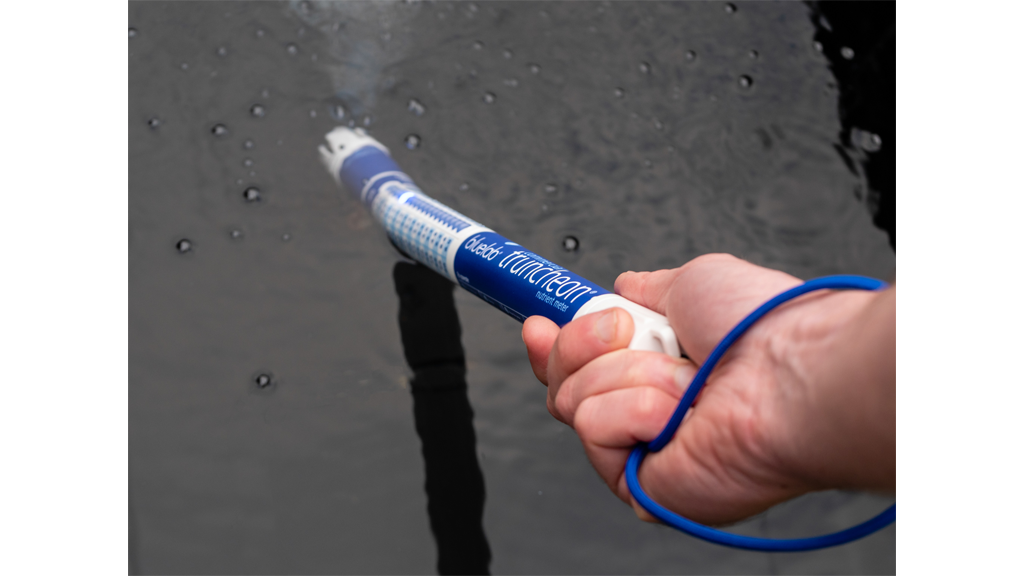
We must monitor and adjust pH daily to keep it in the 5.5–6.5 range. Nutrient solutions are topped up with water as plants consume it, and we replace or replenish the reservoir every 1–2 weeks. A good habit is to monitor both EC and pH with appropriate meters on a set schedule.
Here’s a quick reference table:
| Growing Media | Key Focus | Example Products |
|---|---|---|
| Soil | pH, structure, slow-release fertilisers | Miracle-Gro, compost |
| Coco Coir | Extra Ca & Mg, coco-specific formulas | Canna Coco, Cal-Mag |
| Hydroponics | EC, pH, total nutrient solution control | General Hydroponics, Optimum Hydroponix |
Conclusion
Choosing the right nutrients starts with knowing your plant type and the method of growing you use. Different growing mediums—such as soil, hydroponics, or coco coir—require different nutrient balances. For example, soil often retains nutrients longer, while hydroponics demands precise feeding.
We should always consider our local hardiness zones and planting times. In early spring, roots begin their growth, making phosphorus especially important for kick-starting development. As the season progresses, nitrogen supports leafy growth and potassium aids in overall vigour.
Here’s a quick table to help summarise some main nutrients and their key roles:
| Nutrient | Main Benefit | When Most Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Leafy growth | Early–mid growth |
| Phosphorus (P) | Root and flower development | Early spring, flowering |
| Potassium (K) | Overall plant health | Throughout season |
We also need to remember the role of micronutrients like zinc, iron, and boron. Even in small amounts, these make a significant difference.
At Hyjo, we’re committed to supporting every gardener. We provide expert advice and quality products, so you don’t have to navigate nutrient choices alone.
We encourage everyone to review their own growing method and seasons. If you’re not sure which nutrients fit your setup—or your climate—please get in touch with us for tailored recommendations. Your plants will thank you!






 Store Locator
Store Locator