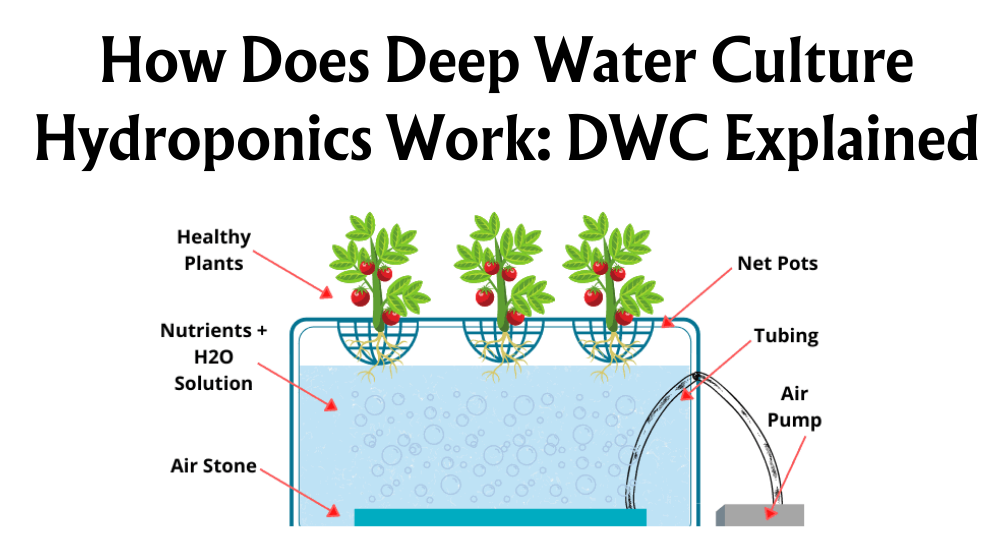
Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, often stirs up questions about health and safety. It's a fascinating innovation that allows us to cultivate crops in a controlled environment while using less water and fewer pesticides. Concerns occasionally arise over whether this high-tech approach differs significantly in terms of nutrient quality compared to traditional soil farming.
We have good news for curious gardeners and health-conscious consumers: hydroponically grown vegetables are just as healthy and safe to eat as their soil-grown counterparts. Studies indicate no substantial nutritional differences, and this method even reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases. Hydroponics provides a sustainable option that aligns well with environmental concerns.
As we explore the realm of hydroponics, we will address common misconceptions and highlight the benefits this farming technique offers. This post aims to give a comprehensive picture of the health implications of hydroponics and guide you toward safe practices.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic vegetables are nutritionally similar to soil-grown ones.
- This method is environmentally friendly by using less water and pesticides.
- Proper practices ensure safety and cleanliness in hydroponic systems.
Are Hydroponic Nutrients Harmful?
Hydroponic nutrients play a crucial role in providing essential minerals directly to plants' roots. This method can raise questions about the safety and composition of these nutrient solutions, so let’s explore some aspects such as the differences between organic and synthetic nutrients, common myths, and the benefits of hydroponic systems.

Organic vs Synthetic
When it comes to organic nutrient solutions, these are derived from natural sources. Examples include fish emulsion and compost teas. They often contain essential components that enrich the nutrient solution, but potential contaminants like pathogens must be monitored closely.
On the other hand, synthetic nutrients are manufactured chemical compounds designed to deliver precise nutrient compositions. An advantage here is their purity and ease of control, which allows us to efficiently regulate nutrient ratios without the unpredictability sometimes associated with organic alternatives.
Myths
One myth suggests that hydroponic nutrients are packed with harmful chemicals. The reality, however, is that these nutrients are carefully formulated and regulated for safety.
Another misconception is that synthetic nutrients are inherently dangerous. They actually offer the benefit of precision in feeding, helping us avoid nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
When used correctly, hydroponic solutions are a safe and reliable way to nourish plants, challenging these widespread myths persuasively.
Benefits of Controlled Nutrient Levels
One key benefit is the precision with which we can tailor nutrient solutions to meet the specific needs of different plants. This precision feeding allows for optimal growth conditions, maximising plant health and yield.
In soilless growing, hydroponics reduces the opportunity for soil-borne diseases and pollutants to affect crops. This not only produces healthier plants but also cuts down on the need for pesticides.
The environmental benefits are noteworthy as well. Efficient use of nutrients reduces runoff, thus minimising the impact on surrounding ecosystems. It makes hydroponics a sustainable alternative for many types of farming, helping us contribute positively to the environment while maintaining robust harvests.
Is Hydroponics Safe For The Environment?
When exploring the environmental safety of hydroponics, several factors come into play. Our focus should be on water usage efficiency, pesticide reduction, energy consumption, and urban farming methods.

Hydroponics significantly reduces water consumption. It utilises up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming, making it a compelling choice for water conservation. This is particularly beneficial in areas prone to drought.
One advantage of hydroponic systems is their controlled environment, which often means we can reduce or eliminate the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides. This reduction can minimise pollution compared to traditional farming methods.
However, energy consumption is a notable consideration. Indoor hydroponic systems may use more energy, especially for lighting. To mitigate this, we can adopt energy-efficient solutions, such as LED lights or tapping into renewable energy sources.
Urban hydroponic farms present an exciting case study. Many cities have successfully implemented these systems, demonstrating their potential for sustainable food production while reducing transportation emissions. This contributes positively to climate change mitigation efforts.
Thus, while hydroponics is not entirely without its challenges, its environmental benefits, particularly in resource conservation and reducing chemical use, make it a favourable alternative to traditional farming in many contexts.
Are Hydroponic Vegetables Safe?
When discussing the safety of hydroponic vegetables, food safety and human health are key considerations. One advantage is the minimal use of pesticides and herbicides due to controlled environments. This often leads to fewer chemical residues compared to traditional farming.

Evaluating Food Safety Concerns
Food safety in hydroponics heavily depends on water quality. It's crucial we utilise clean, contaminant-free water to prevent potential health risks.
System materials also play a role. We must be cautious about materials that might leach harmful substances. Choosing safe plastics and avoiding certain compounds is essential to ensure the produce remains safe for consumption.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Hydroponic plants and produce should adhere to food safety standards. We must follow local and international guidelines to ensure the vegetables meet quality expectations and remain safe for consumers.
Hydroponic systems can potentially bypass soil-based contaminants, providing an edge in ensuring food safety. This practice aligns with various compliance norms that many regions require for food production.
Consumer Perceptions and Realities
There's often a perception that hydroponic produce might lack in traditional nutritional quality. However, evidence suggests otherwise. These vegetables are not only safe but also nutritious, boasting equivalent levels of vitamins and minerals as those grown in soil.
While some are concerned about the absence of soil, the nutrient solutions used are carefully curated. They achieve a balanced mix of essential elements, supporting the plant's growth and safety for human health. Hydroponic vegetables, thus, often offer a fresh alternative with safety checked throughout the cultivation process.
Are Hydroponic Vegetables Healthy?
When it comes to hydroponic crops, the question of health and nutritional value often arises. Hydroponic vegetables, including popular choices like leafy greens, herbs, and peppers, are cultivated in nutrient-rich water solutions. This method offers a unique set of advantages, particularly for urban agriculture.

Comparing Nutritional Profiles
We've all wondered how nutrient composition compares between hydroponic vs. soil-grown vegetables. Current research shows promising results. Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C and iron are found at similar levels in both hydroponically grown and soil-grown produce.
Nutrient Content Analysis
Numerous studies have analysed the nutritional quality of these vegetables. Findings indicate that factors such as light exposure play a crucial role. Artificial light, often used in hydroponics, can influence antioxidants and other nutrients.
Factors Influencing Nutritional Value
-
Light Exposure: Plants grown under artificial light may have different nutritional profiles compared to those grown naturally.
-
Nutrient Solution Composition: Customised nutrient solutions can optimise plant health, offering potential benefits like enhanced vitamin content.
Case Study: Leafy Greens
For instance, leafy greens such as spinach and lettuce have been extensively studied. These studies reveal that hydroponic leafy greens can achieve peak nutrition by controlling water and light conditions. This means we can enjoy fresh, nutritious produce year-round.
The health benefits of choosing hydroponics are evident, especially in areas with limited access to fresh produce. By providing consistent quality and nutrient density, hydroponic farming offers an innovative solution to nutritional challenges.
Hydroponics Sterility
When discussing hydroponics, we often hear about the notion of "sterility." It's easy to assume that hydroponic systems operate in sterile environments. However, this is not quite accurate. While hydroponic growing methods occur in controlled environments, these systems are not devoid of microorganisms.

It's important to recognise the role of microorganisms in plant health. Beneficial bacteria and fungi play crucial roles, such as aiding nutrient uptake and supporting plant resilience. In hydroponic systems, these microorganisms contribute to a balanced ecosystem.
Let's talk about some best practices for maintaining this balance. Regular system cleaning and maintenance are vital to prevent harmful pathogens. Monitoring and managing microbial populations ensure that beneficial microbes thrive, promoting robust plant growth.
Many hydroponic growers also utilise beneficial microbial additives. These products, like certain bacteria and fungi supplements, can enhance microbial health in hydroponic systems by boosting the community of beneficial organisms, improving plant resilience and growth.
One example is the use of specific bacteria that can enhance nutrient absorption. Although these practices vary, the emphasis is always on fostering a supportive microbial environment within our hydroponic setups. With attention to detail, we can harness the benefits of these tiny, beneficial allies effectively.
Golden Rules For Safe Hydroponics
When it comes to hydroponics, prioritising safety is crucial for the health of both plants and consumers. There are some golden rules we can follow to ensure safe practices in our hydroponic garden.

Proper Nutrient Management
- We should regularly monitor and adjust nutrient concentrations. This helps in meeting the plants' nutritional needs.
- Nutrients must be stored in cool, dark places to prevent degradation and maintain their effectiveness.
System Maintenance and Hygiene
- Cleaning and sterilising equipment regularly is essential to prevent pathogen buildup.
- This practice not only safeguards our plants but also ensures a healthy growing environment.
Water Quality Assurance
- To avoid contamination, we must use filtered or distilled water.
- High-quality water is fundamental to the health of our hydroponic systems.
Material Safety
- It's vital to select system components made from food-safe materials.
- This choice helps in preventing harmful chemical leaching into the water and nutrient solutions.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
- Utilising sensors and monitoring tools allows us to track system parameters effectively.
- Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in hydroponic safety keeps our practices up-to-date.
By following these guidelines, we can efficiently manage limited space and create a thriving hydroponic garden that's safe for everyone involved.
Conclusion
We've explored whether hydroponics is bad for our health, and the findings are quite reassuring. According to the latest research, hydroponically grown produce is safe and offers nutritional benefits comparable to their soil-grown counterparts.
One significant advantage is the ability to grow fresh produce in urban areas, reducing food deserts and providing year-round access to healthy options. This is crucial for those living in areas with limited access to traditional farms.
We should focus on implementing best practices to maximise both personal and environmental benefits. Ensuring proper nutrient solutions and managing potential risks of disease are part of this commitment to safety and quality.
The future of hydroponics seems promising. The sustainability and efficiency of this cultivation method mean it holds the potential to revolutionise agriculture. By embracing this innovation, we can work towards a healthier and more sustainable future for everyone.






 Store Locator
Store Locator