How to Set Up Hydroponics with Fish
Have you ever marvelled at the idea of having both a vegetable garden and a pet fish tank in one? Well, it's not a daydream; it's called aquaponics, and we're diving into the finer details of setting one up. Aquaponics is a sublime blend of hydroponic growing and aquaculture that lets us farm fish and grow plants in a closed-loop system. It knocks out the need for soil and chemical fertilizers, making it a champion of sustainability.
Hydroponics on its own is a method where plants absorb nutrients dissolved in water, meaning they can grow faster and in tighter spaces compared to traditional gardening. When we introduce fish into this equation, we get aquaponics. The fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, and in return, the plants purify the water for the fish. It’s a win-win situation that mimics nature's own cycles.
The journey through this guide will unwrap the layers of setting up your own aquaponic system - selecting suitable fish and plant types, designing the setup, and maintaining a healthy environment for both to thrive. It’s a greener, space-saving method for us urban dwellers or those just looking to put fresh, home-grown food on the table. We’re also diving into the upsides and potential hurdles of aquaponics, ensuring you have an honest look at what it takes to bring this synergistic system into your home or garden.
Key Takeaways
- Aquaponics fuses hydroponics and aquaculture to create a soil-free, sustainable growing system.
- The system is environment-friendly, making efficient use of water and space while providing mutual benefits for plants and fish.
- Understanding system design, plant and fish selection, and maintenance is critical for a successful aquaponics setup.
What Is Aquaponics?
This innovative farming approach marries hydroponics (that’s growing plants without soil) with aquaculture (raising fish). Together, they form an eco-friendly duo, making our veggie dreams a reality in a sustainable, closed-loop system.
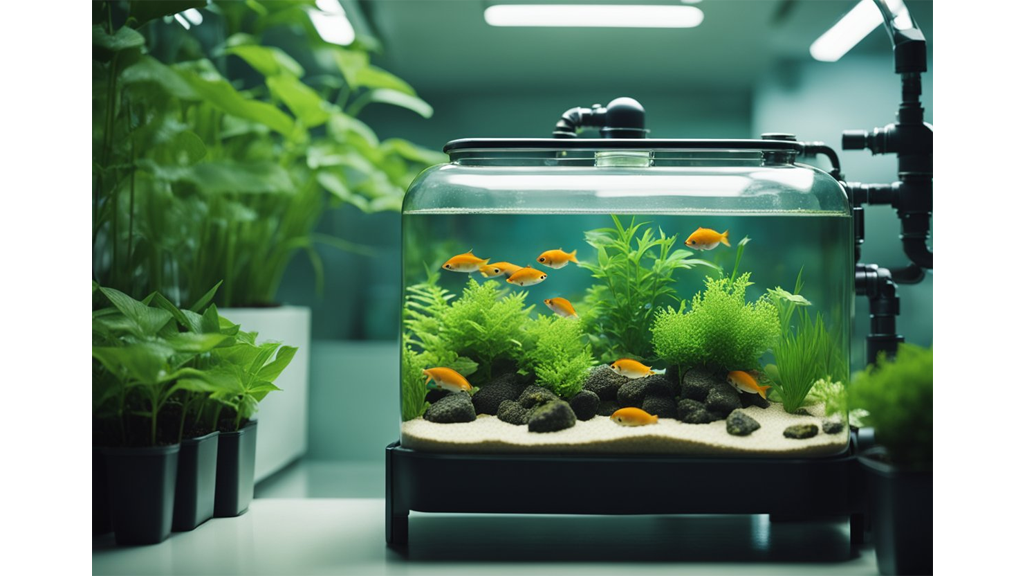

How does it work? Well, our finned friends in the fish tank produce waste, which might sound a bit yucky, but it's actually liquid gold for plants! This waste contains nutrients that plants crave. Imagine the fish saying, "Here, take what I don't need!" and the plants responding, "Cheers, mate! Just what we needed!"
The plants then use these nutrients to grow and, in return, filter and purify the water, which cycles back to the fish. It’s nature’s own recycling process!
Let’s talk residents of this system. Ornamental fish like tilapia or trout are top choices, while plants such as lettuce, spinach, and basil flourish in this setup.
So, why aquaponics? For a start, it's super-efficient, using up to 90% less water than traditional farming. Plus, it’s a real space-saver and can yield produce all year round.
Here's a quick breakdown of the perks:
- Eco-friendly: It's light on the environment.
- Sustainability: It reduces waste and doesn’t need chemical fertilisers.
- Efficiency: It uses resources wisely, saving water and space.
All up, aquaponics is a smart move for us forward-thinking gardeners who like our plants homegrown and our conscience clear.
How Aquaponics Works
Embarking on an aquaponics adventure? We'll get to grips with the intricate dance of fish and plants sustaining each other. Let's jump straight into the nitrogen cycle and the nuts and bolts of the system components.
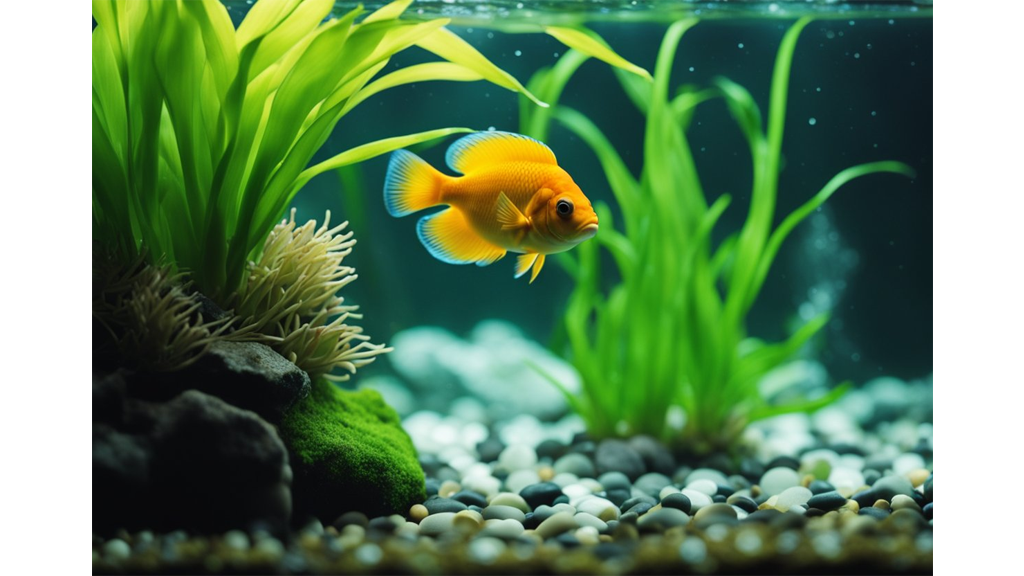

The Nitrogen Cycle
Imagine our fish swimming happily in their tank. They eat, they excrete waste, and that's where the unseen magic begins. Fish waste contains ammonia, a compound that's not great for them, but it's a starting point for our nitrogen cycle. Beneficial bacteria come into play here, converting this ammonia into nitrite and then into nitrate—a nutrient our plants adore. By absorbing these nitrates, plants essentially purify our water, which cycles back clean and oxygen-rich to our fishy friends.
Key steps of the Nitrogen Cycle:
- Fish Waste Production: Our fish produce waste that contains ammonia.
- Bacterial Conversion: Beneficial bacteria convert ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate.
- Plant Absorption: Plants take up nitrate, which in turn cleans the water for fish.
Understanding this cycle is vital, as it maintains the water quality and supports plant growth. Keep a keen eye on the levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to ensure your aquatic ecosystem stays healthy.
System Components
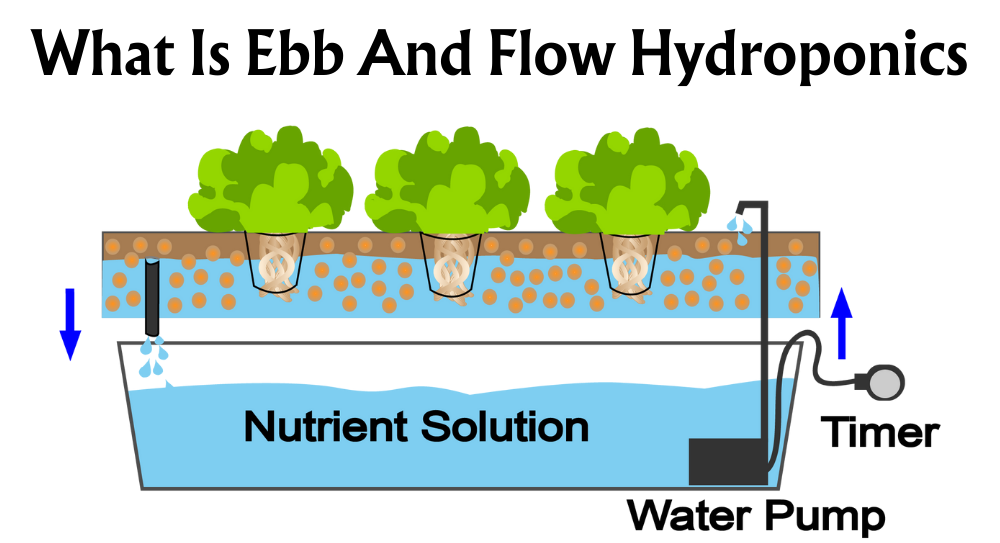
First off, we need a fish tank—a watery residence for our aquatic pals. Size matters, so consider the space. We then require a plant bed where our green companions will thrive. Positioning is key; we fancy a spot with ample light and appropriate temperature.
To connect our aquatic duo, a series of pipes and tubes are necessary, along with a pump to facilitate the stately waltz of water. Fill your fish tank with water, add your fish (mind the species and quantity), and then turn your attention to populating the plant bed with a suitable growing medium and favoured plants.
Components Checklist:
- Fish tank: Contains your chosen fish species.
- Plant bed: Holds growing medium and plants.
- Pump: Moves water from the fish tank to the plant bed.
- Filter: Cleans water by removing solid waste.
- Bacteria: Converts ammonia into nitrate.
- Siphon: Drains water back to the fish tank.
Remember, balance is the name of the game. Monitoring pH and temperature, along with preventing the bane of algae and pests, will set us on the path to aquaponics mastery. It's a constant learning curve, but the results are as rewarding as they are fascinating.
Advantages of Aquaponics

Ever thought about how we can grow our food more smartly? Imagine a system where our scaly friends, the fish, help our greens thrive. That's aquaponics for you – a blend of aquaculture and hydroponics that’s making waves in sustainable food production.
Space-Saving Marvel: Aquaponics is known for its spatial efficiency. We can produce significantly more food in less space compared to traditional farming. It's perfect for urban areas where space is at a premium.
Water Wise: Love the thought of saving water while gardening? Us too! Aquaponics systems recycle water, using up to 90% less than conventional gardens. The fish produce nutrient-rich water that's pure gold for plant growth, limiting the need for synthetic fertilisers.
-
Reduced Chemical Use: Here’s where we all breathe a sigh of relief – aquaponics naturally sidesteps the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides. Healthy fish and plants all the way!
-
Boosts Yield: By providing constant and readily available nutrients, plants in an aquaponic setup often grow faster, boosting our yields. Hello, abundant harvests!
-
Sustainable Food Production: We're talking about a remarkably sustainable cycle. Fish waste provides food for plants, while the plants clean the water for the fish. It’s a win-win environment for both.
-
Benefits to the Environment: Aquaponics is kind to Mother Earth. By reducing the runoff of nutrients and pollutants, we're looking after our waterways too.
Disadvantages of Aquaponics
We know aquaponics can be an innovative method of growing plants and fish together, but let's chat about some of the snags we might hit along the way.

Upfront Costs: Starting an aquaponics system isn't cheap, pals. We're talking about a significant initial investment here – tanks, pumps, filters, grow beds, and more are all on the shopping list. Plus, we need the know-how to put it all together. Fancy diving into your piggy bank and doing a bit of homework?
Electricity Dependence: Ever had a power cut at the worst possible moment? Aquaponics systems depend heavily on electricity. Pumps, filters, and siphons – they all need power to keep everything ticking over. If they fail or if we have an outage, it's more than just the lights that go out; water flow stops, water quality drops, and our fishy friends and plants might start feeling a bit under the weather.
Fish and Plant Limitations: Think of aquaponics as a somewhat exclusive club. Not all fish and plants are keen on joining. We've got to be choosy to find the right match, and some might say it's a bit of a headache. Plus, there's the drama of fish diseases, pesky parasites, and those uninvited predators that fancy a fishy feast or a leafy lunch.
Maintenance: Roll up your sleeves because keeping an aquaponics system healthy takes work. We've got to keep an eye on our underwater allies – the beneficial bacteria. They're the unsung heroes that convert fish waste into plant food. Slack on monitoring, and things can go south fast.
So, it's not all sunshine and rainbows with aquaponics. It's a commitment, and like all relationships, it's going to have its ups and downs. The dream of a harmonious, self-sustaining home aquaponics? It's possible, but we've got to weigh the cons before taking the plunge.
Starting an Aquaponics System
Setting up an aquaponics system is an exciting adventure into sustainable farming, where fish and plants grow together in harmony. By following these steps, we can construct our own ecosystem that provides fresh vegetables and potentially a protein source.
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Gather Your Materials: We'll need a fish tank (aquarium, barrel, or bucket), a grow bed (tray, tub, or box), a pump (submersible or air pump), filtration system (sponge, gravel, or biofilter), siphon (bell, loop, or timer siphon), and a growing medium (gravel, clay pebbles, or coco coir). Don't forget tools like a drill, saw, scissors, and a marker for assembly.
-
Preparation: Using our marker and drill, mark and drill holes where the pipes and tubes will connect the fish tank to the grow bed.
-
Cut and Attach: Cut pipes and tubes to the appropriate length with our saw and scissors. Attach pipes and tubes to the pump, filter, siphon, fish tank, and grow bed.
-
Set Up the Fish Tank: Place the tank in the desired location, fill it with water and introduce our chosen fish. Tilapia, trout, or goldfish are brilliant choices due to their hardiness.
-
Add the Grow Bed: Fill our grow bed with the selected growing medium. Position it so it can drain back into the fish tank.
-
Planting: Now's the time for planting seeds or seedlings in the grow bed. Lettuce, spinach, and basil are not only delicious but grow well in aquaponics systems.
-
Starting the System: Plug in the pump and siphon to ensure water flows properly from the fish tank up to the grow bed and back down. We need to test the setup for leaks and ensure the water quality is safe for both fish and plants.
Choosing the Right Fish and Plants
The species of fish and plants you choose are crucial for the health of your aquaponics system:
-
Fish Choices: We should pick species that we actually fancy and that thrive as aquarium fish. Tilapia are warm-water fish that grow fast and are quite tasty, while trout prefer cooler waters.
-
Plant Selection: Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and herbs generally do well in aquaponics systems. These are easy to grow and maintain but also remember, heavier feeders like tomatoes will need a more mature and balanced system.
Remember, balance is key; we need to ensure that the number of fish and the plant load are compatible to keep our little ecosystem thriving without extra inputs.
Types of Aquaponic Systems
When we think about bringing together fish and plants in a harmonious dance of aquaponics, we're spoilt for choice. Each system is a world of its own, tailored to specific fish or plants, and moulded by the space it will inhabit.

Media-Based Systems
Imagine a bed of clay pebbles or gravel cradling the roots of your plants. This is the essence of media-based aquaponics, a steadfast choice especially for those just dipping their toes into the world of aquaponics. We flood these beds, and then a siphon draws the water back to the fish, taking the nutrient-rich waste with it for a beautiful cycle that mimics traditional farming methods. It's simple, reliable and a fantastic all-rounder that can support a diverse range of plants and fish.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Next up is the Nutrient Film Technique. Picture a gentle stream carrying a thin film of water and nutrients directly to the plants' eagerly waiting roots. We see this method featuring channels or pipes with plant roots suspended inside, making NFT a sleek pick for those aiming to go big with leafy greens and herbs. A bonus is its efficiency, which makes it a darling of commercial growers looking to maximise their space and yield.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
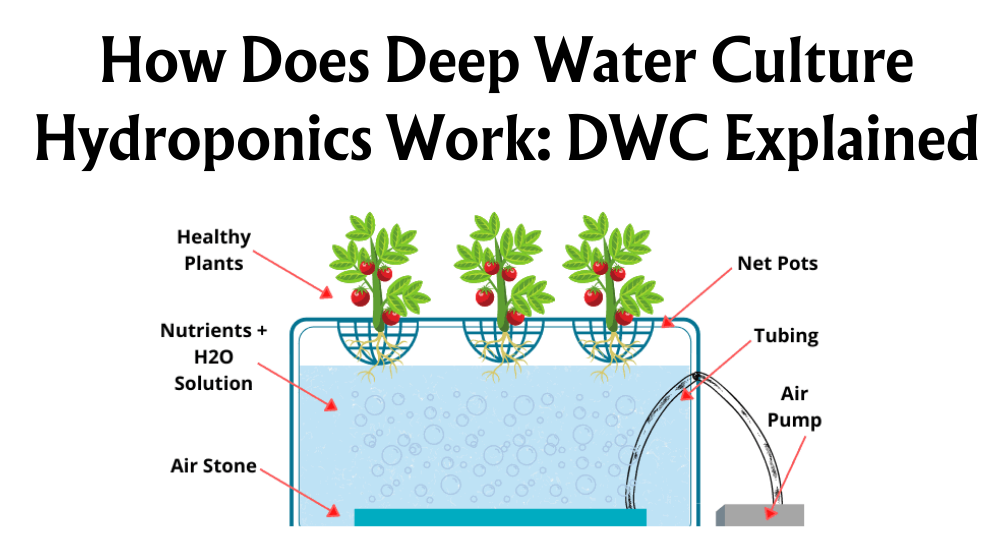
Last but definitely not least is Deep Water Culture or DWC. With this technique, we're immersing plant roots directly into a nutrient-rich bath with an air stone bubbling away to keep oxygen in the mix. It's like a spa for plants! Net pots keep the plants afloat as they soak up everything they need from the water below. DWC often results in rapid growth and high-quality produce like lettuce and kale, making it a favourite for those who like to push the envelope in plant cultivation.
Each of these systems shines in its own way and choosing one over the other rests on what we want to achieve. Are we crafting a personal green space at home, or are we fuelling a commercial venture? Our plants, our fish, our goals—they all have a say in the aquaponic system that will work best for us.
Fish and Plant Choices
When starting your aquaponics adventure, it's super important to choose the right fish and plants. We want to add fish that can handle our fiddling while we're learning the ropes, and plants that are grateful for the nutrients without being too fussy, right?

Best Fish for Aquaponics
Let's chat about fish first! You want species that are not only sturdy but also friendly to your local climate and have good growth rates. Here's a peek at the top contenders:
- Tilapia: A real favourite, they're tough, grow quickly, and can handle less-than-ideal water conditions. They're happy in warm water and are a lovely addition to your food production line-up.
- Trout: These chaps prefer cooler water but they grow swiftly and are fantastic for cooler climates. Plus, they're a treat for dinner!
- Catfish: With their whiskered faces, these bottom dwellers are a hardy bunch. They don't mind murky water and can get pretty chunky with time.
- Koi and Goldfish: While not typically a top choice for the dinner plate, these fish are perfect for demonstrating the beauty of aquaponics and they're as tough as old boots.
Each fish contributes to a thriving ecosystem by producing waste that's packed with beneficial bacteria – a free lunch for our plants! But don't forget, fish health is paramount; happy fish equals a happy garden.
Favoured Plants in Aquaponics
Now, let's talk greenery. We're after plants that say "Thank you!" to those fishy nutrients and grow with gusto. Let's take a gander:
- Lettuce: It's practically the poster child for aquaponic gardens. Loves the water-based nutrients and doesn't make a fuss.
- Herbs: Fancy some fresh basil or parsley? Many herbs thrive in aquaponics, making our kitchens smell and taste great.
- Vegetables: From leafy greens to crunchy cucumbers, a variety of vegetables can prosper in an aquaponic system.
Our plant pals and our finned friends work in harmony, creating a closed-loop ecosystem where plant health enhances food production and the plants, in turn, keep the water clean for the fish.
Maintaining Your Aquaponics System
Let's keep our underwater garden thriving, shall we? Regular maintenance of our aquaponics system is crucial for the health of both the fish and plants. We've got to keep an eye on water quality, ensure the equipment is running smoothly, and monitor the health of our fish.

Daily Checks
Water quality: We can't overstate the importance of this! Every day we need to:
- Check pH levels, aiming for 6.8 to 7.2 for most systems.
- Look out for changes in water clarity and colour.
- Keep an eye on the odour. Fishy smells aren't just a metaphor; they're a real sign something might be off.
Fish Health: Happy fish need a happy garden. So let's:
- Observe our fish for activity levels and appetite. Lethargic or disinterested fish are a red flag.
- Make sure they are feeding properly. If they aren't, it could be a sign of stress or poor water quality.
Routine Maintenance
Filters: The unsung heroes keeping our water crystal clear. We should:
- Regularly clean or replace mechanical filters.
- Check biological filters for healthy bacteria levels—these little guys are vital for breaking down fish waste.
Equipment: Our aquatic allies. To ensure they perform their best, we need to:
- Inspect pumps and pipes for any signs of wear or blockage.
- Ensure heaters and thermostats are working correctly to keep that water temp just right.
Remember, maintaining aquaponic systems is all about balance! A bit of effort every day keeps our fishy friends frolicking and our garden growing gorgeously. It's a win-win!
Conclusion
As we ventured through the intricacies of marrying hydroponics with fish farming, we discovered an impressive synergy. Our eco-friendly approach to food production not only yields healthier plant life but also promises a sustainable future for us all.
Here's a recap of what we've discussed:
- The aquaponic system creates a closed loop where fish waste fertilises plants, and in turn, the plants purify water for the fish.
- Starting with a basic setup of a fish tank, grow bed, water pump, and plumbing is manageable even for beginners.
- The system is glaringly scalable, inviting us to start small and dream big without constraints aside from the physical space.
Should doubts arise about the practicality or efficiency of such a system, let's consider that aquaponics consumes a mere 15% of the water compared to traditional soil farming and increases yield by 60% per square foot. It's no small feat!
Now, for a few handy tips and tricks:
- Ensure you have adequate light and space for both the tank and your plants.
- Cycle the system well to establish those crucial beneficial bacteria.
- Choose the right plants—lettuce, herbs, or strawberries are excellent starters.
In terms of potential objections, we might ponder the complexity or initial cost. However, the long-term benefits and the joy of harvesting your own crops and fish outweigh these considerations. Plus, it’s a step towards our collective goal of a healthier planet.
So, are you ready to dive into this eco-friendly adventure? Let's build a greener, more sustainable world, one aquaponic garden at a time.






 Store Locator
Store Locator