As agriculture continues to evolve, many are curious about how modern techniques compare to more traditional methods. Hydroponics is a growing method that replaces soil with water and nutrients, allowing us to cultivate plants in environments where traditional farming methods might struggle. This technique saves space by using vertical growth systems, providing an efficient alternative in urban areas or regions with limited arable land.
Traditional farming, on the other hand, has been our age-old practice for centuries, deeply rooted in utilising soil to nourish and make plants grow. It often requires larger expanses of land, which can pose challenges for small-scale farmers or those facing land scarcity. Although it may come with the advantage of lower initial setup costs, it demands careful management of land resources to ensure sustainable productivity.
Our article aims to dive into the fundamental differences between hydroponics systems and traditional farming. We will explore various aspects like cost, resource utilisation, and environmental impact, offering insights for both seasoned growers and gardening enthusiasts interested in these distinct agricultural practices.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water, optimising resource use in smaller spaces.
- Traditional farming relies on soil, requiring more land but involves lower setup costs.
- This article compares both methods for insight on cost, efficiency, and impact.
Hydroponics
In hydroponics, we grow plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions. This method has advanced over time, providing efficient use of space and resources and enabling year-round cultivation.

Types of Systems
1. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
We use a thin film of nutrient solution that flows continuously over plant roots. Advantages include efficient nutrient delivery, especially for crops like lettuce. Disadvantages arise from its vulnerability to pump failures, which can quickly affect plant health.
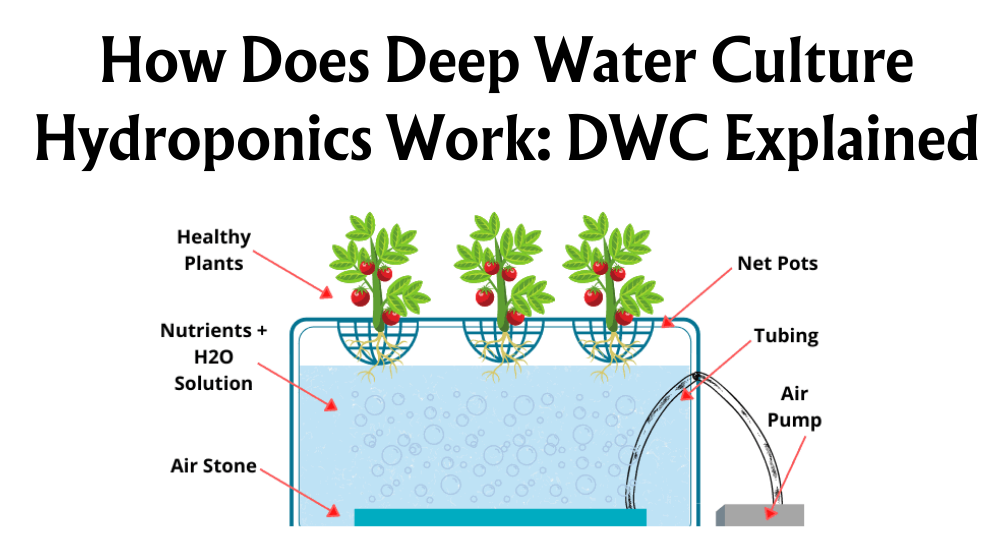
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
In this system, roots are suspended in an oxygenated nutrient solution. Advantages involve its simple setup and rapid plant growth. Disadvantages include difficulties with temperature control, which can affect nutrient uptake.
3. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
The grow bed is periodically flooded and then drained. Advantages include versatility, accommodating different plant sizes. Disadvantages require precise timing and monitoring to prevent over or under watering.
4. Drip System
We deliver nutrient solutions directly to the plant roots through drippers. Advantages are its controlled nutrient delivery and scalability. Disadvantages involve potential for clogging, necessitating regular maintenance to ensure system efficiency.
5. Aeroponics
In aeroponics, roots are misted with nutrient solutions. Advantages include maximum oxygen exposure and rapid growth rates. Disadvantages stem from the high maintenance needs and sensitivity to system failures, which demand close attention.
Traditional Farming
Traditional farming, or soil-based agriculture, involves cultivating crops in natural environments and has played a crucial role throughout history. This method remains fundamental in providing food and sustaining livelihoods worldwide. By understanding its components, we can appreciate the intricate balance necessary for successful crop production.

Components of Traditional Farming
Soil Preparation
Proper preparation is vital, involving tilling, fertilisation, and pH adjustment. Healthy soil enhances crop yields by improving structure and fertility. Tillage loosens soil, incorporates organic matter, and controls weeds, while fertilisers—either organic or chemical—supply essential nutrients. Monitoring soil pH helps in creating a favourable environment for plant growth.
Planting and Growing
Seed selection, sowing techniques, and plant spacing are integral to traditional farming. Crops depend heavily on seasonal cycles, impacting growth and productivity. Aligning planting schedules with these natural rhythms maximises yield. Spacing allows plants to access ample sunlight and nutrients, preventing competition.
Pest and Disease Control
Managing pests and diseases often involves pesticides, crop rotation, and natural predators. Crop rotation reduces pest buildup by alternating plant families. Although chemical pesticides are effective, they must be used judiciously to minimise environmental impact. Natural predators like ladybirds can also help manage infestations.
Fertilisation
Fertilisation practices vary, with organic options like compost and chemical products. Adequate nutrient management ensures robust crop growth. Organic fertilisers improve soil health over time, while chemical solutions provide immediate nutrient boosts. Balance is key in maintaining productive fields.
Irrigation
Irrigation techniques include drip, sprinkler, and flood irrigation, all facilitating water distribution. Drip irrigation conserves water by directly applying it to roots, whereas sprinkler systems mimic natural rainfall. Water conservation is critical in areas facing scarcity issues. Proper irrigation bolsters plant health and yield.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
Harvest timing and methods affect crop quality and longevity. Techniques vary, from manual picking to mechanised methods, impacting post-harvest outcomes. Proper storage maintains quality, extending shelf life. Efficient post-harvest handling ensures minimal loss and maximum product value.
Key Comparisons: Hydroponics Vs Soil

Water Usage
- Hydroponics: We utilise up to 90% less water because of recirculation.
- Traditional Farming: There's higher water consumption with risks of runoff and evaporation.
Space Efficiency
- Hydroponics: Vertical farming allows us to plant more densely, using less space.
- Traditional Farming: Requires extensive land areas, limiting flexibility.
Yield and Growth Rate
- Hydroponics: We enjoy faster growth and higher yields due to controlled environments.
- Traditional Farming: Yields depend on soil quality and climate conditions.
Environmental Impact
- Hydroponics: There's reduced pesticide use and soil erosion, but energy consumption is higher.
- Traditional Farming: Risks include soil degradation and pesticide runoff.
Nutrient Control
- Hydroponics: We can manage nutrients precisely for optimal plant health.
- Traditional Farming: Nutrient availability varies, based on soil conditions.
Pest and Disease Management
- Hydroponics: Lower risk since our environment is controlled.
- Traditional Farming: Plants are more exposed to pests and diseases.
Energy Consumption
- Hydroponics: We experience higher energy use for lighting and climate control.
- Traditional Farming: Relies on natural sunlight, using less energy.
Let's examine how these points affect our choices in crop production. Hydroponics offers resource efficiency and reduced water usage, making it viable in areas with water scarcity. Meanwhile, traditional methods might sustain crop diversity but face challenges with land degradation and giving consistent yields.
Which Is Cheaper?

When we're talking about initial investments, hydroponics demands a heftier upfront cost. This includes expenses for setting up systems, like pumps, lights, and growth beds. On the other hand, traditional farming, particularly on a small scale, typically starts with lower initial outlays for basic tools and seeds.
Operational costs differ significantly between the two methods. For hydroponics, we continuously pay for energy, nutrient solutions, and system upkeep. These can add up, especially with complex setups.
In contrast, traditional farming incurs ongoing expenses for seeds, fertilisers, and pesticides. We also need to account for labour, which can be significant depending on the farm's size and scale.
Long-term considerations reveal interesting dynamics. Hydroponics has the potential for higher profitability thanks to increased yields and the ability to produce crops year-round. This could offset those steep initial costs in time.
Conversely, traditional farming faces challenges like market fluctuations and environmental unpredictability. Crops may suffer from weather extremes or pests, affecting profitability. This unpredictability can lead to varying profit margins that require close management.
While both hydroponics and traditional farming have their own financial nuances, each offers unique benefits and challenges that suit different goals and markets. It really depends on what we're aiming for in terms of scale, resilience, and investment style.
Conclusion
In our exploration of hydroponics and traditional farming, we found each method offers unique benefits and challenges.
Hydroponics allows us to grow plants in nutrient-rich water, eliminating the need for soil. This technique enables farming in urban environments, utilising vertical spaces, water efficiency and growing indoors. Hydroponics can be particularly beneficial when aiming for food security in areas with limited arable land.
On the other hand, traditional farming remains vital due to its adaptability to various climates and its historical significance in agricultural practices. This technique often involves lower initial costs compared to hydroponics, making it accessible for smaller farms.
In considering the environmental impacts, hydroponics typically uses less water than traditional farming. This can play a crucial role in addressing climate change and reducing food waste by controlling the growing environment more precisely.
Both methods can contribute significantly to agricultural production. As we move forward, combining these approaches may provide innovative solutions to feed our growing population sustainably.
With these insights, we can continue to refine our farming techniques, optimising them for efficiency and sustainability while ensuring reliable food supply systems.






 Store Locator
Store Locator