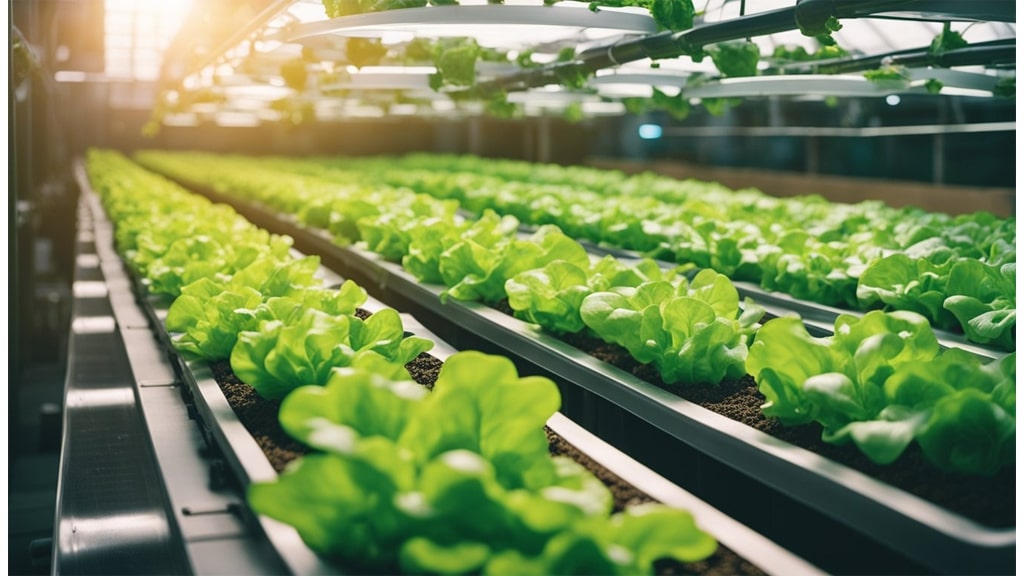
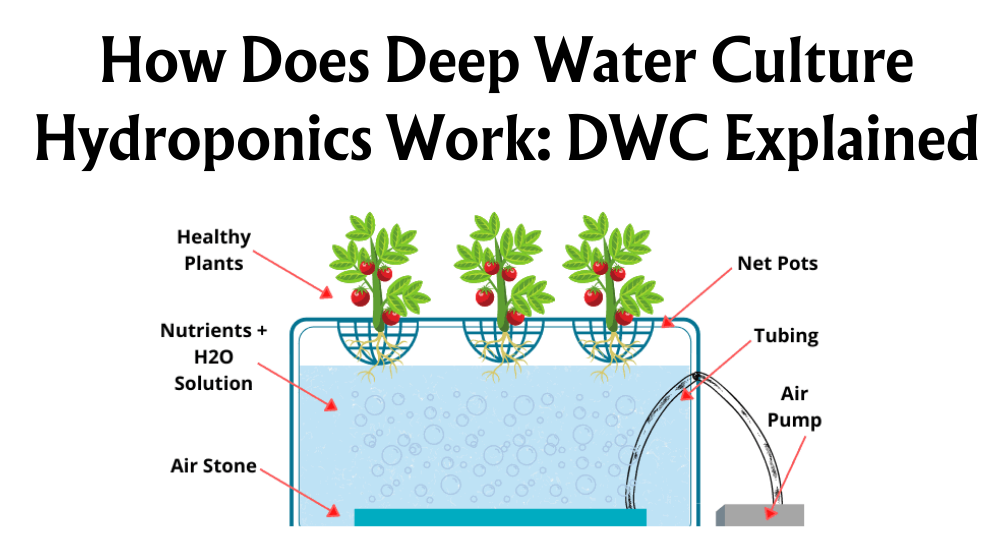
Hydroponic gardening fascinates us with its promise of vibrant growth and year-round productivity. As we explore this innovative method, the question that often arises relates to its scope: Can all plants be grown hydroponically? The straight answer is no; while the majority of plants respond well to hydroponic systems, there are exceptions. Each plant has unique needs, and not all are suited to this soil-less environment.
Our journey into hydroponics opens up a world of possibilities for growing an array of vegetables, herbs, and even flowers. Many plants, including popular choices like tomatoes, lettuce, and strawberries, thrive in this controlled environment. The absence of soil presents opportunities for many plants but also challenges for specific varieties that require more robust structures or specific soil conditions.
As we delve deeper, we'll uncover which plants make great candidates for hydroponic systems and which might struggle. It's a fascinating exploration, bridging the gap between traditional gardening and modern technology, and we're excited to guide you through it.
Key Takeaways
- Not all plants are suitable for hydroponic growth.
- Vegetables, herbs, and some flowers flourish hydroponically.
- Exceptions include species needing specific soil conditions.
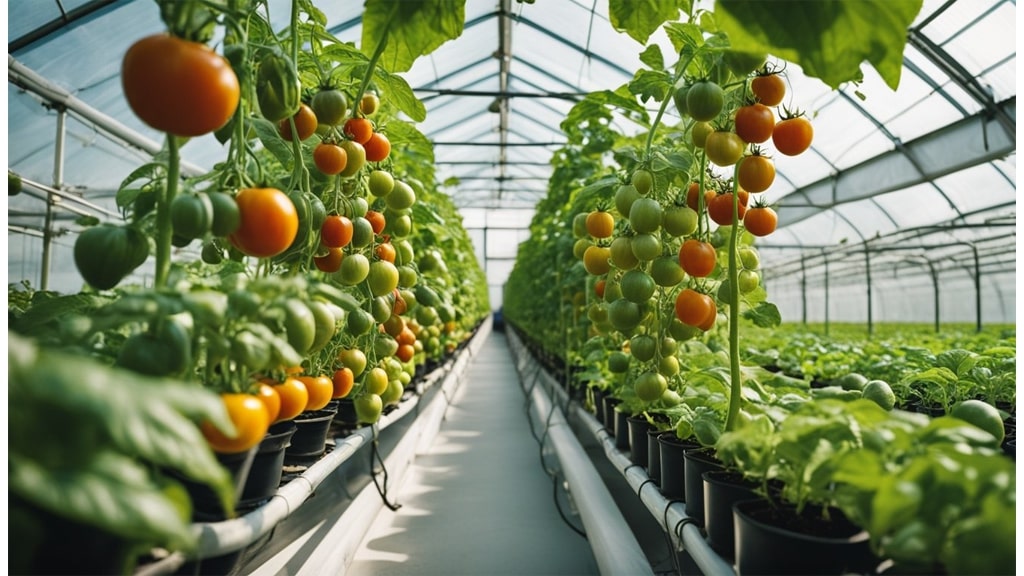
What Kind of Vegetables Can Hydroponics Grow?
Many vegetables thrive in hydroponic systems, offering us an efficient way to cultivate fresh produce indoors or in constrained spaces. Understanding which vegetables flourish can help us maximise our hydroponic gardens.
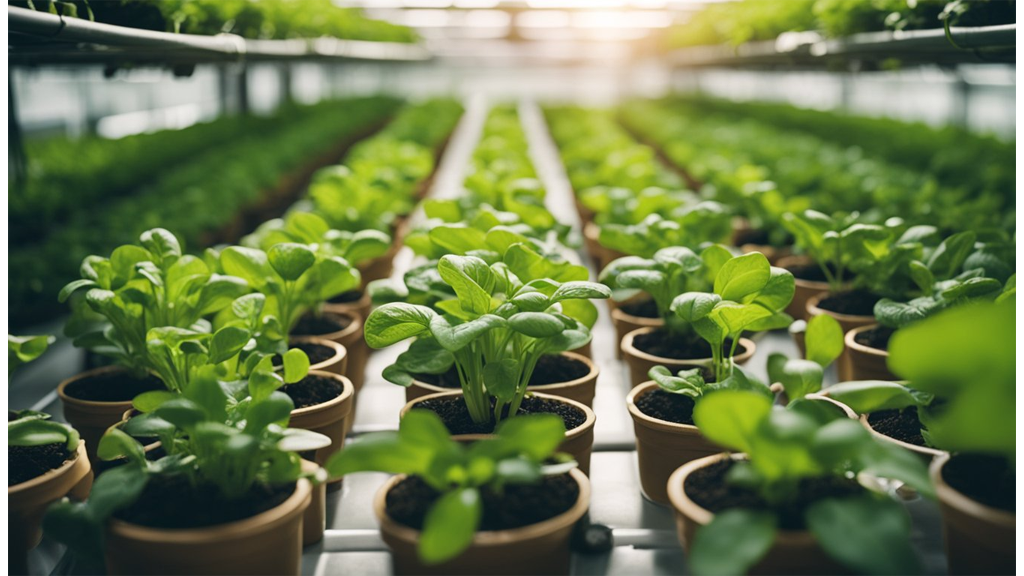

Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are ideal for hydroponics due to their rapid growth and high water content. Our go-to choices include:
- Lettuce: Varieties like romaine, butterhead, and leaf lettuce adapt well, allowing continuous harvests. For a detailed guide on hydroponic lettuce and growing it, check out our in-depth blog.
- Spinach: This nutritious green grows efficiently in our hydroponic setups.
- Kale: Robust and adaptable, kale provides us with multiple harvests.
Fruiting Vegetables
For those interested in fruiting vegetables, a few options are perfect for hydroponics, though they may need extra care:
- Tomatoes: Cherry and grape varieties are particularly well-suited, offering a delicious crop.
- Peppers: Both sweet and hot varieties can flourish, given proper care.
- Cucumbers: Opt for dwarf or bush varieties, which fit perfectly in our systems.
By selecting the right vegetables, we can ensure a bountiful and varied hydroponic garden. With attention and care, many of our favourite veggies can thrive without soil, providing fresh produce all year-round.
Can You Grow Herbs in Hydroponics?
Herbs are perfect for hydroponic systems. They bring fresh flavours to our kitchens all year round, using up very little space.
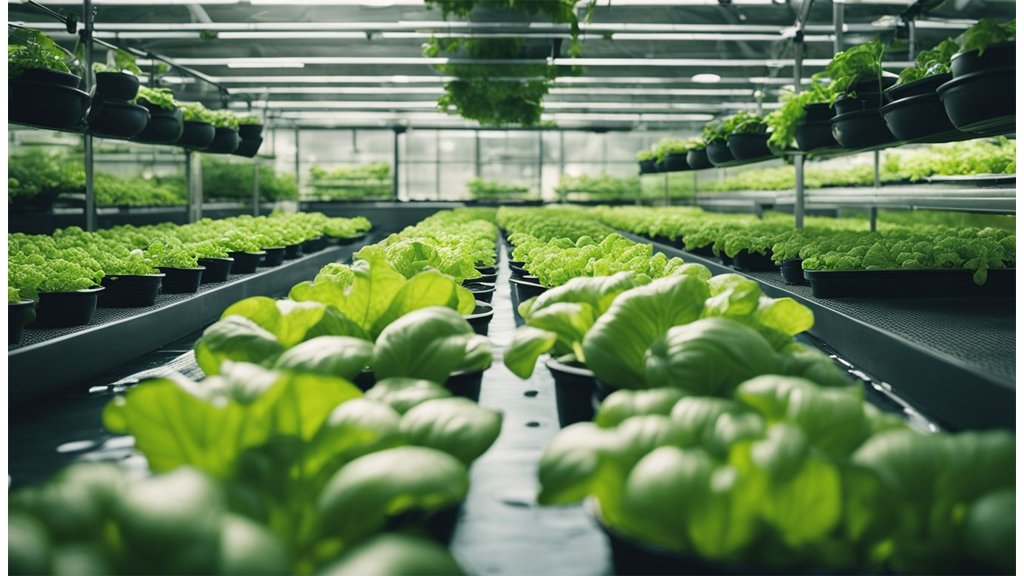

Basil thrives when grown hydroponically. This herb is a standout choice for indoor gardening enthusiasts due to its rapid growth and fragrant leaves.
Mint is another excellent option for hydroponics. It grows vigorously, and the controlled environment of hydroponics helps contain its spread effectively, which can be a challenge in traditional gardens.
Cilantro is versatile in hydroponic settings. We can propagate it in water for immediate use, but for an extended harvest, cultivating it from seeds in hydroponic systems is highly effective. We have an in-depth blog on hydroponic herb growing for your perusal.
Here’s a brief list of other herbs to consider for hydroponics:
- Thyme: Offers its aromatic, earthy flavour with relatively low maintenance.
- Oregano: Provides robust taste, supporting diverse culinary uses.
- Chives: Give a mild onion flavour, making them a versatile addition to dishes.
- Parsley: Easy to grow and perfect for garnishing various meals.
Hydroponic cultivation of herbs not only saves space but also ensures optimal conditions such as nutrient-rich water and controlled environments, making it a sustainable choice for urban gardeners seeking convenience and flavour.
Can You Grow Flowers Hydroponically?
We can absolutely grow flowers hydroponically, and it can be a rewarding experience. Many ornamental plants adapt well to soilless systems, providing us with a fulfilling way to enjoy blooms indoors all year round.
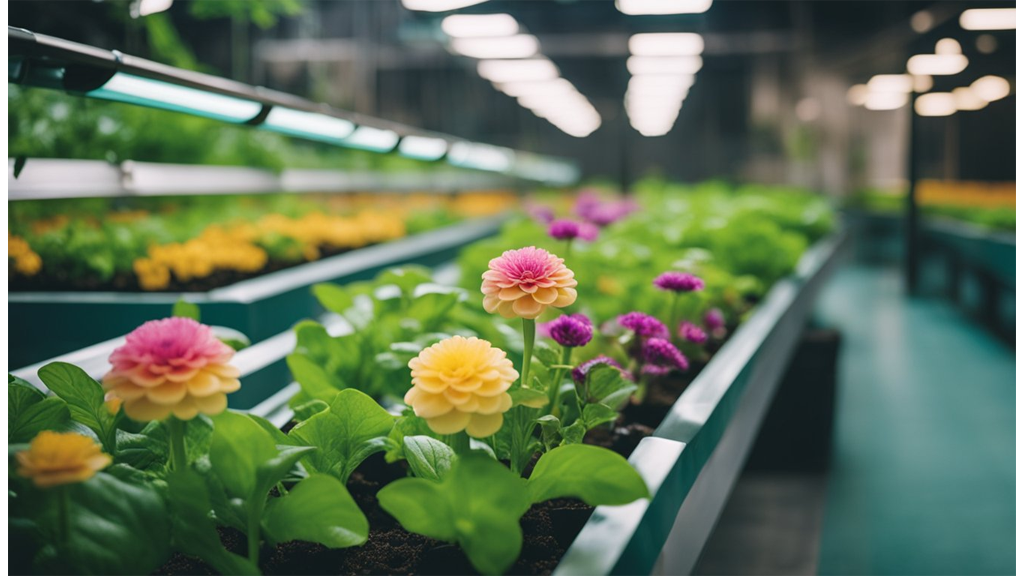

Orchids are a favourite for hydroponic systems because they naturally thrive in similar conditions. These stunning plants often prefer the controlled environment we can provide, mimicking their epiphytic nature.
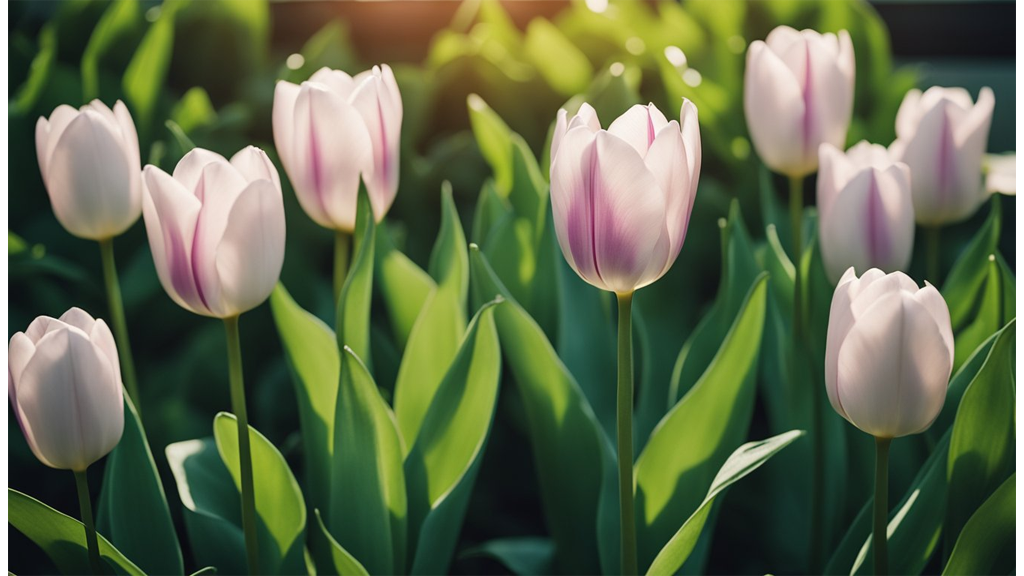
We love Petunias for their vibrant colours and adaptability. They're perfect for hydroponics, especially when paired with proper lighting to boost growth and blooming. Another flower that thrives in hydroponic conditions is the tulip, for which we have an extensive blog on.
Marigolds are another great choice. These cheerful flowers not only bring colour but can also help with pest control within our indoor gardens, adding both beauty and utility.
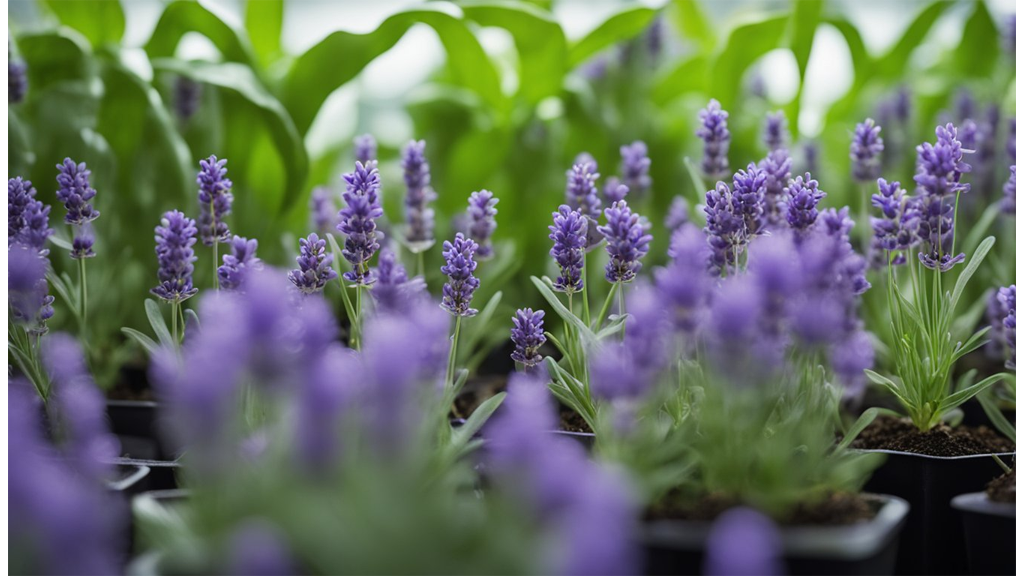
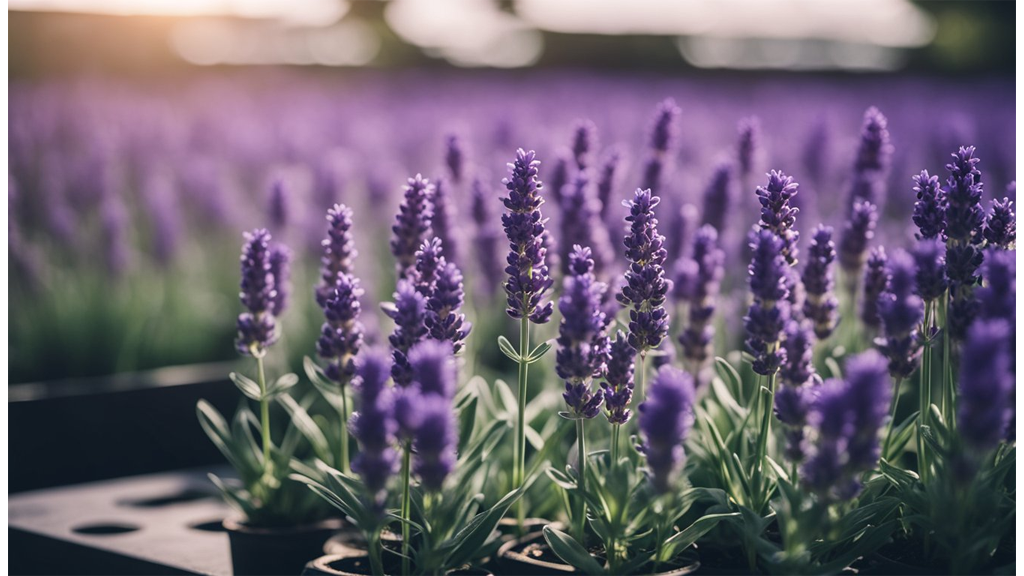
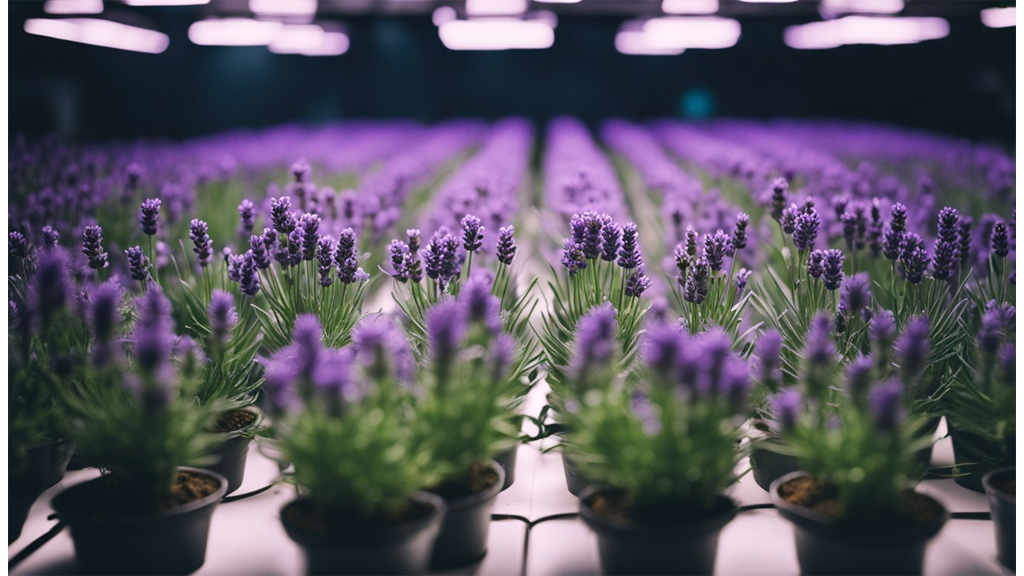
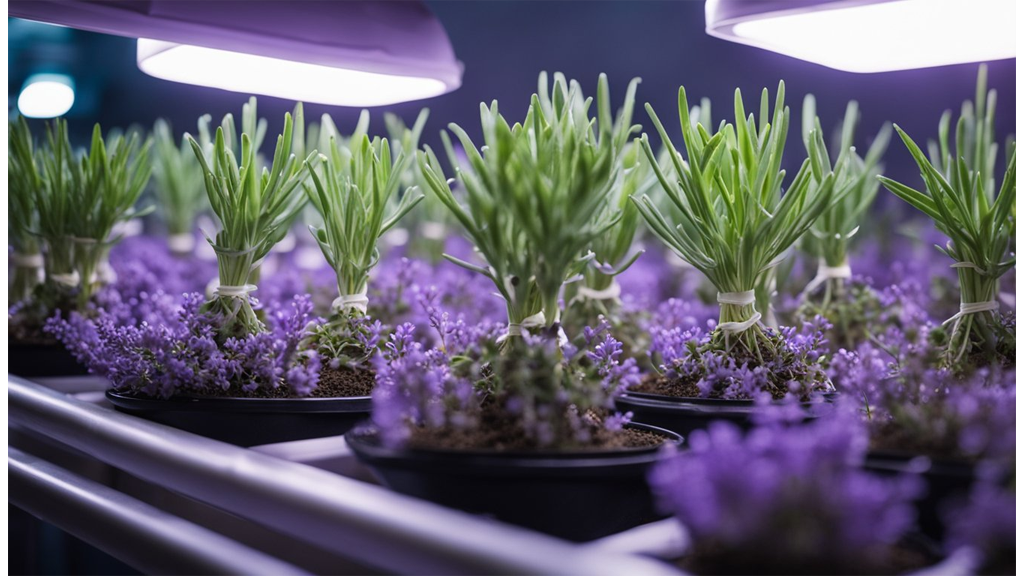
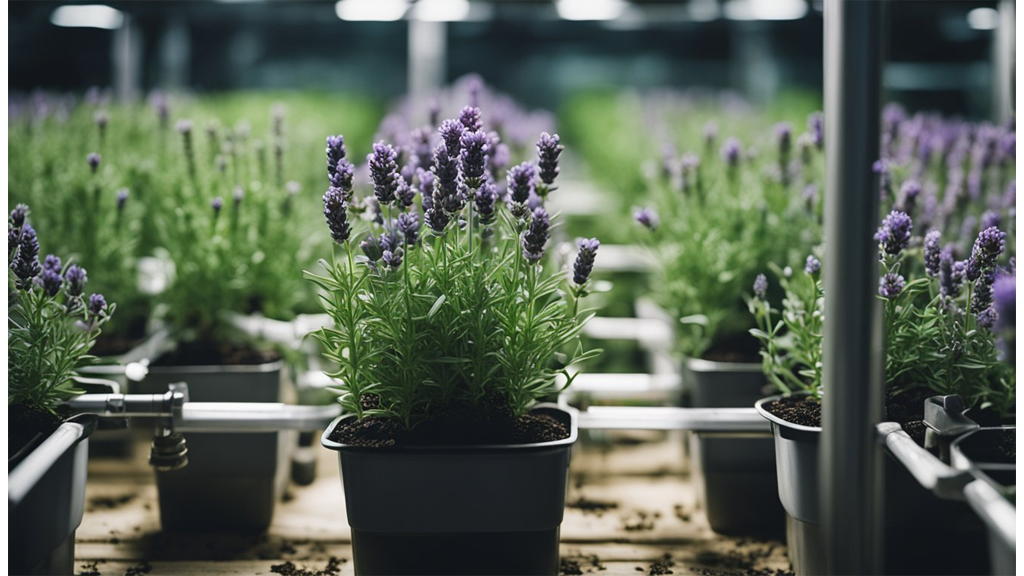
Lavender is another flowering plant that does well in hydroponic growing conditions. For a deep dive on hydroponic lavender, check out our latest blog.
Here's a quick table to summarise:
| Flower Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Orchids | Thrive naturally in soilless systems |
| Petunias | Flourish with proper lighting |
| Marigolds | Aids in pest control, adapts well |
Hydroponics allows us to grow a wide range of flowers, bringing the garden right into our home. It's fascinating to witness their growth and development in a controlled environment.
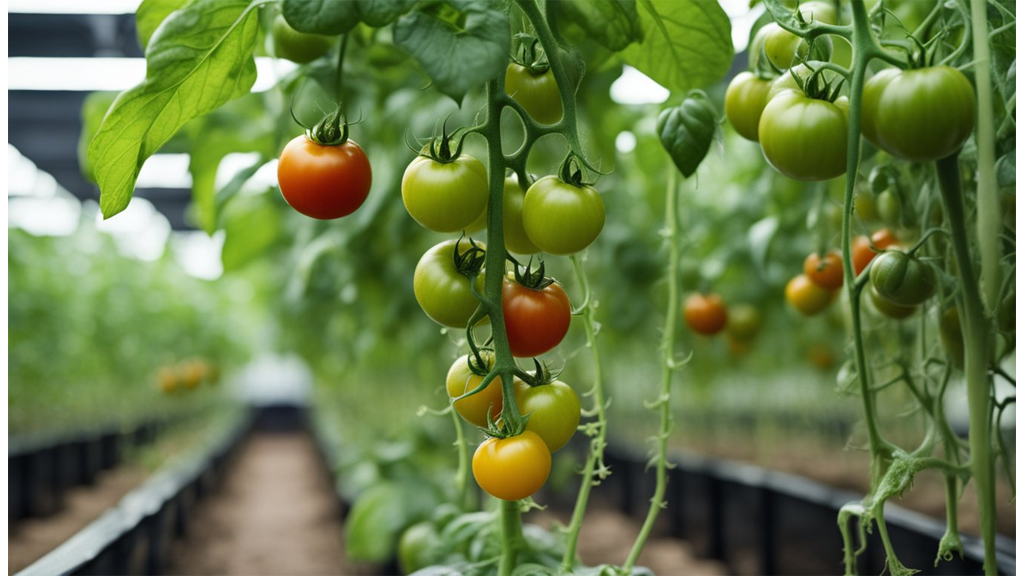
Can You Grow Tomatoes With Hydroponics?
Growing tomatoes hydroponically is entirely feasible and offers great results when approached thoughtfully. It's quite popular among hydroponic enthusiasts due to the prolific yields and controlled growth conditions that this method affords.
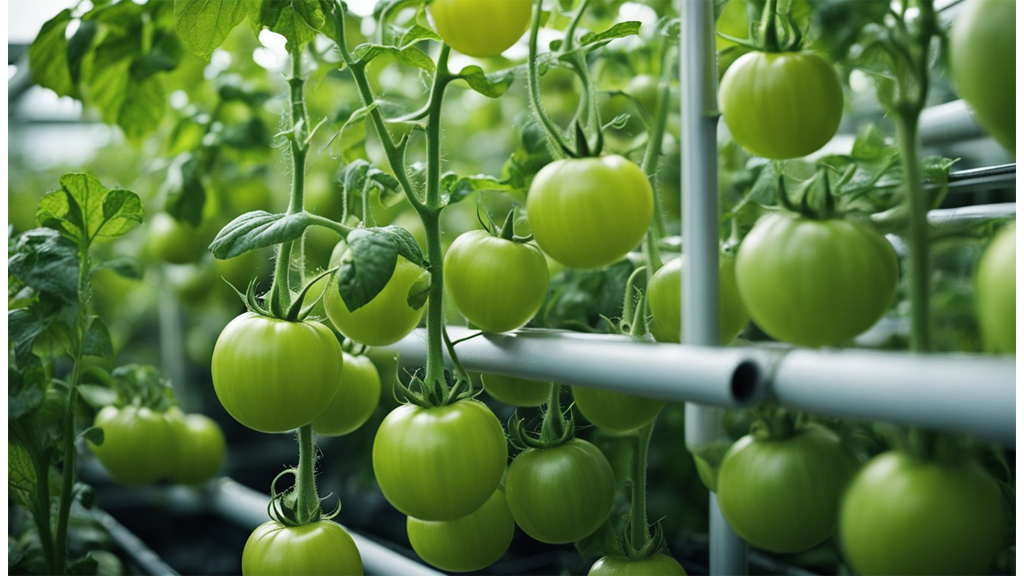

Variety Selection:
When choosing tomato varieties, it's wise to opt for determinate or dwarf types. These are well-suited for indoor systems as they have a more compact growth habit that fits limited spaces nicely.
Pollination Needs:
In a hydroponic setup, natural pollinators, like bees, are often absent. We might need to engage in manual pollination to ensure a good fruit set. This can be easily achieved by gently shaking the plants or using a soft brush to transfer pollen.
Support Structures:
Tomato plants, especially as they begin to bear fruit, require support to handle the weight. Providing trellises or stakes is crucial. Doing so helps maintain structure and prevents damage to both the plant and its fruits.
Indoor and Outdoor Cultivation:
Tomatoes can be cultivated in hydroponic systems both indoors and outdoors. Careful nutrient selection is important for achieving vibrant growth and juicy tomatoes.
List of essentials for setting up a hydroponic tomato system:
- Rock Wool or another medium like coconut coir
- Nutrient solutions tailored to tomato growth
- Net cups
- Adequate lighting (especially for indoor setups)
Engaging in hydroponic tomato farming can be quite rewarding with delicious results. We have a comprehensive blog on hydroponic tomatoes for a deep dive on how they are grown and the best varieties for doing so. As always, paying attention to the details can result in bountiful harvests year-round.
Can You Grow Spinach In Hydroponics?
Yes, we can grow spinach in hydroponic systems, and it comes with notable benefits. Spinach is well-suited for hydroponics, taking advantage of several features these systems offer. We have an extensive blog on hydroponic spinach, detailing the pros and cons and the best systems for growing.
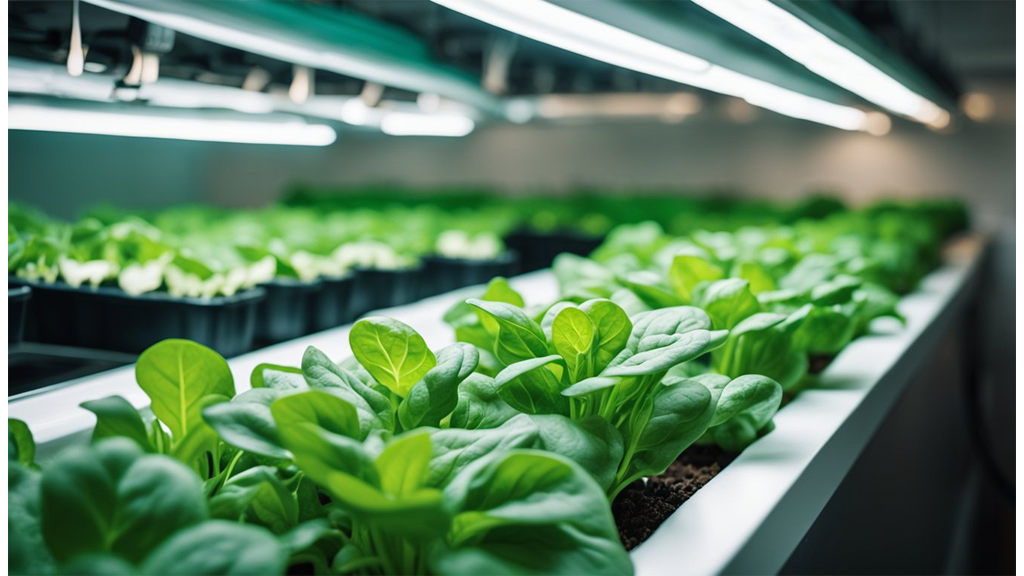

Growth Cycle
Spinach has a fast growth cycle, which means we can expect multiple harvests. This characteristic makes it a practical choice for those looking to maximise their yield over time.
Nutrient Requirements
Balanced nutrient solutions are crucial. Spinach thrives with mixes rich in nitrogen. We must ensure these nutrients are available to support robust growth, especially during the early stages.
Temperature Control
Spinach prefers cooler temperatures. Maintaining an optimal environment can enhance the yield and quality of the crop. Temperature regulation is easier in hydroponics, allowing us more control over the growth conditions.
Advantages
- Consistent growth rate
- Easier pest control
- Reduced soil-borne diseases
Challenges
- Prone to bolting in warmer conditions
- Requires careful monitoring of pH and nutrient levels
Growing spinach hydroponically may pose some challenges, as it's more difficult than cultivating other leafy greens like lettuce. Yet, with attention to detail, spinach can flourish beautifully in a hydroponic setup.
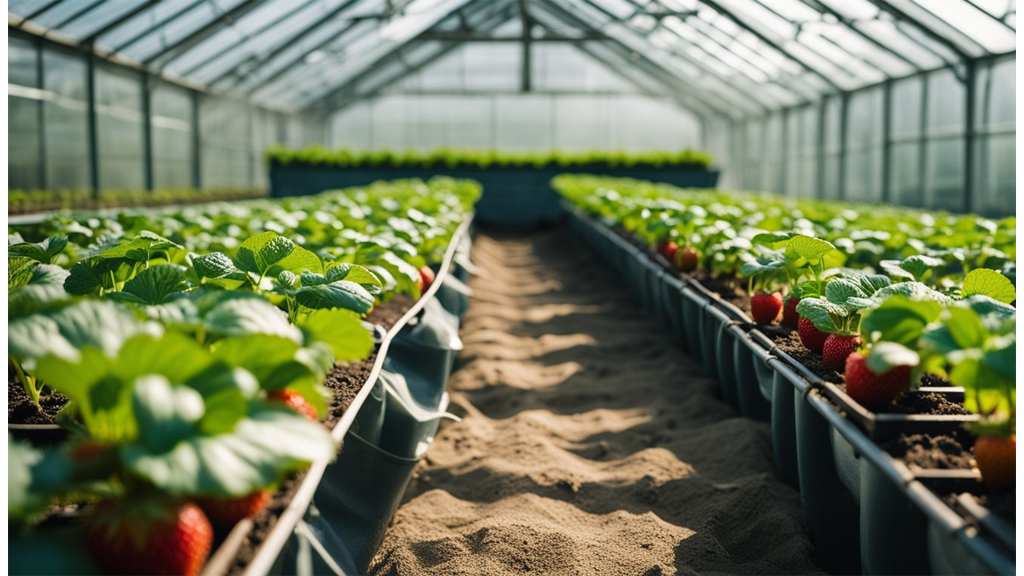
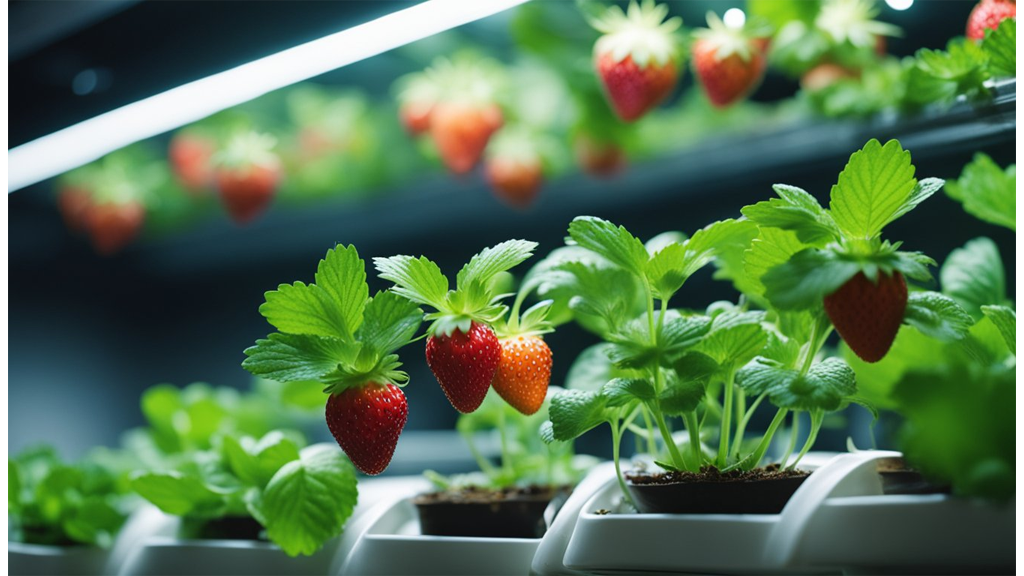
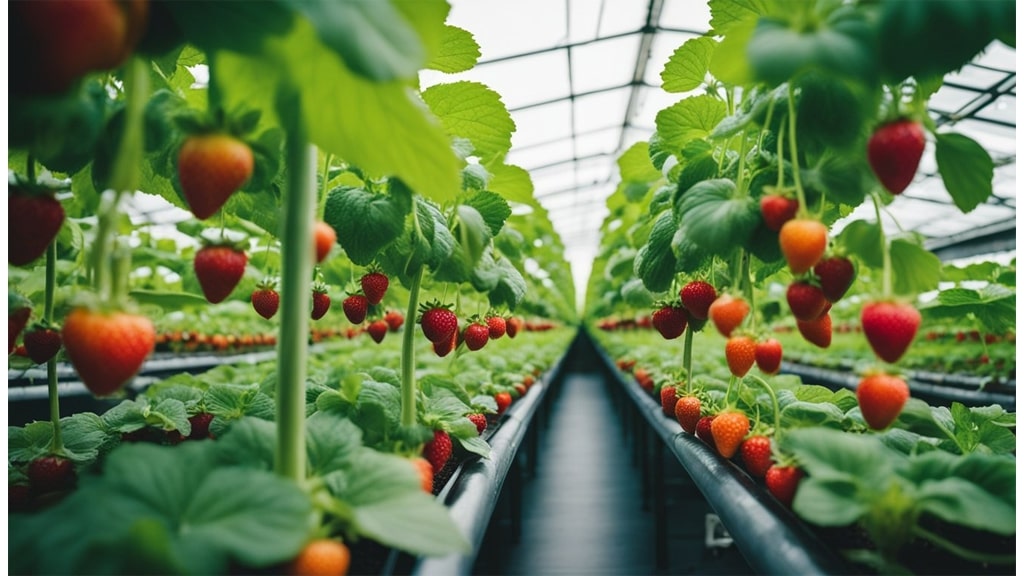
Can Strawberries Grow In Hydroponics?
Yes, strawberries can indeed thrive in a hydroponic environment. This innovative method of cultivation allows us to enjoy fresh strawberries regardless of the season or outdoor conditions.
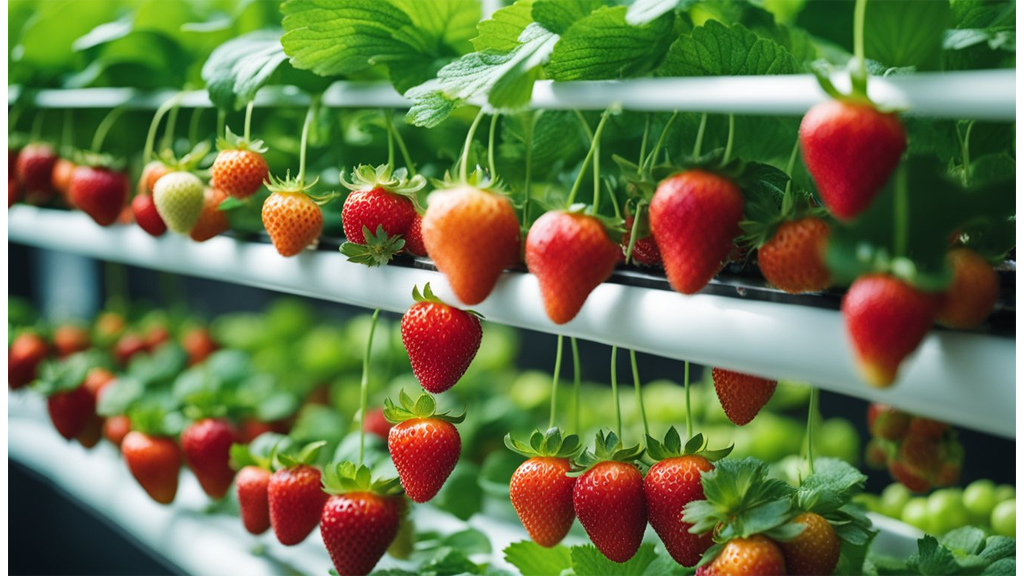

System Choice:
For strawberries, the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is commonly preferred. This system ensures a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water over the plant roots, providing optimal growth conditions.
Varieties to Consider:
Day-neutral or everbearing varieties, such as 'Albion' and 'Monterey', are ideal due to their consistent fruit production. These types don't rely on specific day lengths to bear fruit, making them perfect for hydroponics.
Pollination Process:
Within an indoor set-up, strawberries rely on manual pollination or the introduction of pollinators to ensure fruit development. This crucial step helps in achieving a bountiful harvest.
By controlling factors like nutrition, light, and temperature, hydroponics offers an efficient way to cultivate strawberries. We have an extensive blog on cultivating hydroponic strawberries for a deeper dive on the matter. This method ensures rapid growth and healthier plants.
What Cannot Be Grown Hydroponically?
While the adaptability of hydroponic systems is impressive, some plants don't suit these setups well. Let's explore a few categories that present challenges.

Root Vegetables: Carrots, potatoes, and onions have deep root systems. Accommodating these in standard hydroponic setups can be difficult due to space and support limitations.
Large Fruit Trees: Growing large trees indoors is impractical, especially when considering their need for extensive space and structural support. The typical hydroponic environment isn't equipped to handle these demands.
Vining Plants: Vines like pole beans and peas stretch extensively. While possible, supporting their growth exceeds the capabilities of conventional hydroponic systems. They require more space and sturdy supports.
It's important to remember that each plant has unique needs. For those less suited to hydroponics, traditional soil methods might be the best option.
Conclusion
We love the world of hydroponics and the possibilities it brings to gardening. While not all plants can flourish in a hydroponic environment, many vegetables, herbs, and flowers do exceptionally well, making it an exciting option to explore.
Some plants, like lettuce, tomatoes, and basil, are famously successful in hydroponic systems. These thrive due to their adaptable root systems and minimal soil requirements.
On the other hand, plants with large root systems or those requiring extensive support, like trees or shrubs, may struggle in a water-based system.
It's essential that we tailor our hydroponic setups to meet specific plant needs. With the right nutrients, light, and environment, we can unlock the full potential of hydroponic gardening. By continuously learning and experimenting, we maximise our success and enjoy healthy, productive crops.






 Store Locator
Store Locator