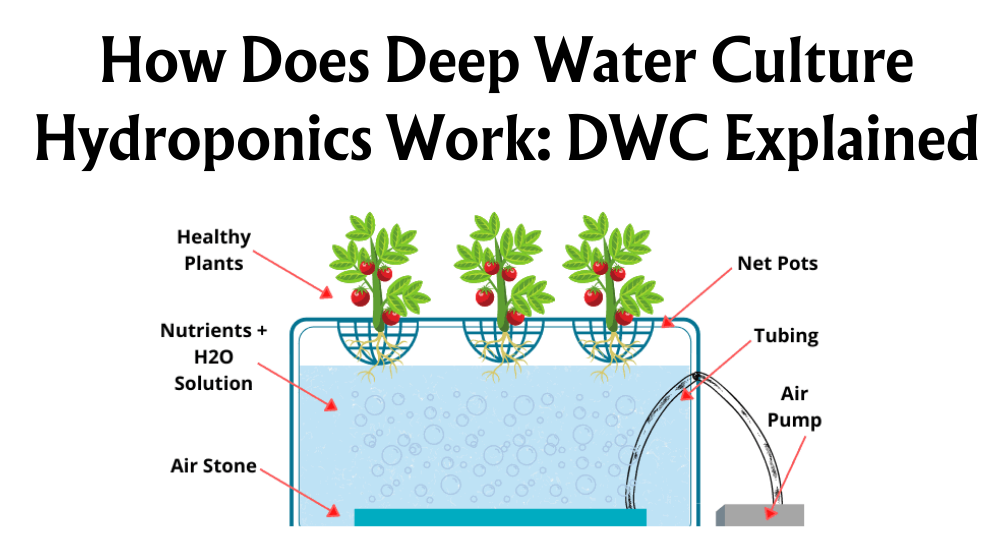
Ventilation plays a crucial role in gardening and hydroponic systems, ensuring plants receive the right amount of air circulation to thrive. When it comes to choosing the right fan for your setup, AC (Alternating Current) and EC (Electronically Commutated) fans are at the forefront. AC fans are known for their simplicity and durability, while EC fans offer higher efficiency and precise control. Understanding the differences between these fan types can help us make informed decisions.
AC fans operate on alternating current and are often praised for their robust construction. They're great for basic ventilation needs but come with higher energy consumption. On the other hand, EC fans utilise electronic commutation, allowing for variable speed control and reduced power usage. This makes them particularly appealing for those of us looking for energy-efficient options.
Switching to the right fan can impact both operating costs and system performance. While AC fans are cost-effective upfront, the long-term savings from the efficiency of EC fans can be substantial. Evaluating these differences can guide us to the most suitable choice for our gardening and hydroponic systems.
Key Takeaways
- AC fans provide simplicity and durability.
- EC fans offer efficiency and control.
- Choice impacts costs and system performance.
How Do Fan Motors Work?
Fan motors are at the heart of axial fans, providing the necessary motion for effective ventilation and cooling. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling cooling systems to operate efficiently. This process involves crucial components such as electromagnets and rotors.
Electromagnets play a key role by creating a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. This field interacts with the rotor, causing it to spin and thereby generating rotational motion. The rotor is connected to fan blades, which then move air to decrease static pressure and improve air circulation.
Understanding how fan motors work is essential for selecting the right fan for HVAC or refrigeration applications. Different fan motors cater to varying needs, with DC cooling fans often preferred in certain settings due to their efficient power use and adaptability to voltage fluctuations.
When we choose fans, we should consider their power source, efficiency, and intended application. Direct knowledge of motor functionality ensures optimal fan selection, boosting performance in cooling and ventilation processes.
Fan motors differ not only in design but also in performance attributes, impacting areas like cooling and efficiency. Whether supporting an air conditioning system or enhancing airflow in a computer, fan motors are integral to many cooling applications. By understanding their mechanics, we ensure that these cooling fans deliver reliable service in any situation.
What Is An AC Fan Motor?
Definition and Functionality
AC motors run directly on alternating current from the mains supply. In the UK, these motors operate at a frequency of 50 Hz. This means the electromagnets inside switch polarity 50 times a second. This constant polarity change allows AC fans to spin and provide airflow.
Advantages of AC Fans
- Cost-effective: Manufacturing AC fans is generally more affordable due to their simple design.
- Widespread availability: AC fans are widely accessible, making them easy to find when you need a replacement.
- Ease of Maintenance: Simplicity in construction means fewer parts that can wear out.
Limitations of AC Fans
- Limited Speed Control: AC fans have basic speed control capabilities, which can be a drawback for specific applications requiring precision.
- Energy Consumption: They typically consume more energy compared to newer fan types like EC fans, impacting energy efficiency.
What Is An EC Fan Motor?
An EC fan motor is a modern marvel in fan technology, blending the efficient operation of a DC motor with the ease of use found in AC systems. We like to think of it as having the best of both worlds. At its core, an EC motor uses electronic commutation to convert AC input into DC internally.
With an integrated intelligent control module, these motors offer high efficiency and precise speed control. It’s fascinating to see how brushless maintenance-free motors can adjust their speed with great precision. This intelligent design also contributes to energy efficiency.
The installation of EC axial fans can lead to quieter operations, which our indoor gardening enthusiasts will appreciate. We enjoy the fact that reduced mechanical stress translates to a longer lifespan for these motors.
Although they command a higher initial investment, the benefits are substantial. The transient response and ability to maintain constant power and speed makes them a preferred choice for environments requiring high precision. However, let’s not overlook that their complexity in design may sometimes require specialised maintenance.
In essence, EC fan motors offer a unique combination of high intelligence and functional adaptability. The integration with a DC power supply ensures that we can utilise these innovations towards creating an energy-efficient and versatile solution.
Side-by-Side Differences

Energy Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency, EC fans have a clear advantage. They use brushless DC motors, which are more efficient than AC fans. AC fans typically run at a constant speed, while EC fans adjust their speed based on demand, leading to significant energy savings.
Speed Control
EC fans offer better speed control, allowing us to adjust the fan speed precisely to meet our needs. This flexibility can lead to improved energy efficiency. On the other hand, AC fans often have limited speed options, making them less adaptable to varying scenarios.
Noise Levels
If noise reduction is a priority for us, EC fans are typically quieter due to their smooth and consistent operation. They exhibit lower vibration levels, contributing to reduced noise. In contrast, AC fans, with fixed speeds, may produce more noise, especially in environments where noise control is critical.
Maintenance Requirements
EC fans generally require less maintenance because they contain fewer moving parts. This leads to improved reliability over time. AC fans, in comparison, may need periodic checks to ensure ongoing performance, making EC fans a more convenient option for long-term use. Also, the reduced vibration in EC fans results in less wear and tear.
Cost Differences Of AC & EC
Initial Investment
Comparing the initial costs, EC fans tend to have a higher upfront price. This is due to their advanced technology and energy-saving capabilities. On the flip side, AC fans are generally more affordable initially, making them a budget-friendly option for immediate needs.
Operational Costs
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in ongoing expenses. EC fans consume less power because of their ability to adjust speed based on demand, resulting in lower electricity bills. In contrast, AC fans often run at a fixed speed, leading to potentially higher energy costs over time.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Though EC fans are pricier at the start, they offer significant savings on energy bills. This often results in shorter payback periods. For example, we might recoup the additional investment in EC fans in a few years due to reduced operational costs, making them cost-effective in the longer run.
Maintenance
When it comes to maintenance, EC fans usually require less frequent servicing thanks to their modern design. AC fans may need more attention, potentially leading to higher maintenance expenses.
Installation
Installation costs can vary. EC fans, with their sophisticated systems, might need specialised installation, increasing initial expenses slightly. Conversely, AC fans often have simpler setups, which may reduce installation expenses for us.
How To Set Fan Speed?
When adjusting the speed of an AC fan, we can use methods like voltage reduction. While cost-effective, it can lead to limited control over speed and possible fan inefficiency. Variable frequency speed regulation is another option, but it's often more complex and expensive.
For EC fans, adjustments are more intuitive. They come with integrated electronic controls allowing for precise speed settings. This means we can easily set fan speed using an intelligent control system that optimises operation and energy use.
Proper fan speed settings have significant benefits. For instance, they can enhance energy efficiency by reducing power consumption when full speed isn't necessary. This not only saves energy but also extends the fan's life. By doing so, we can ensure our environment remains comfortable and sustainable.
Fan speed settings also impact our plant health, as regulated speeds help maintain optimal environmental conditions. Using a soft start can reduce initial strain on the fan, preventing wear and tear over time. This is another reason speed control is valuable: it fosters equipment longevity.
With a bit of attention to how we control fan speed, we can improve efficiency and performance significantly.
Conclusion
AC fans, or Alternating Current fans, draw power directly from an external source and are known for their simplicity and lower initial costs. These fans are prevalent in settings where upfront budget is a concern. Conversely, EC fans, or Electronically Commutated fans, offer impressive energy efficiency and speed control by converting AC power to DC.
When selecting between these two types, it's crucial to assess specific gardening scenarios and budget considerations. For small gardens, where energy cost isn't a significant concern, AC fans might suffice due to their affordability.
In contrast, large-scale gardens needing consistent power and efficiency benefit greatly from EC fans. The energy savings and precise control can outweigh the initially higher investment.
We should encourage considering long-term benefits and energy efficiency when choosing fans. Though EC fans come with a higher initial cost, their reduced power consumption can lead to substantial savings over time.
It's essential to weigh immediate budget constraints with potential savings in energy costs to make the best decision. This ensures not only optimal performance but also sustainable gardening practices. Let’s make informed choices for our gardens today.






 Store Locator
Store Locator